What is an achiral compound?
What are achiral compounds? A molecule or ion is achiral if it is superimposable, i.e. it can be superimposed on its mirror image. Achiral molecules have a plane of symmetry or a centre of symmetry. Achiral molecules having a stereocenter are known as Meso molecules.
Which of the following compounds is achiral?
1 Answer. Hexane-3-ol is a symmetrical molecule with no chiral carbon hence it is achiral.
How to know if a compound is chiral or achiral?
A test for achirality is the presence of a mirror plane within the molecule. If a molecule has a plane within it that will cut it into two symmetrical halves, then it is achiral. Therefore, lack of such a plane indicates a molecule is chiral. Compounds that contain a single stereo-center are always chiral.
What is the difference between chiral and achiral molecules?
Chiral compounds are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, whereas achiral is superimposable over their mirror images. A compound is said to be a chiral compound when it does not have a plane of symmetry and center of symmetry.
What is called chiral compound?
If any combination of translations or rotations cannot superimpose the molecule’s image on its mirror counterpart, the molecule is said to be chiral. The compounds in which Chiral Centre is present are called chiral compounds.
Are all meso compounds achiral?
Achiral compound: A compound that can be superimposed on its mirror image. The difference lies in the presence of the chiral centre. All meso compounds are achiral (due to internal compensation as you have mentioned) but all achiral compunds aren’t meso.
What is an example of an achiral object?
Achiral objects do not have a handedness, for example, a baseball bat (no writing or logos on it), a plain round ball, a pencil, a T-shirt and a nail. The chirality of an object is related to its symmetry, and to this end it is useful to recognize certain symmetry elements that may be associated with a given object.
Do achiral compounds have symmetry?
Achiral molecules are symmetrical and as a result they are identical to their mirror images. One feature of achiral molecules is that they have a mirror plane of symmetry.
Is every achiral compound optically active?
Chiral compound is optical active. Achiral compound is optical inactive. The sample containing a chiral compound rotates the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light, and the direction and angles of the rotation depend on the nature and concentration of the chiral substances.
Is a compound achiral if it has no chiral centers?
Yes, a compound can be chiral even though it has no chirality centres.
Can a molecule be achiral but have chiral centers?
Substances that have chiral centers but are themselves achiral are called meso compounds. The condition that makes possible the existence of meso compounds is an appropriate degree of molecular symmetry. There are several kinds of such molecular symmetry.
How do you classify chiral or achiral?
In chemistry, an object is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. Conversely, an achiral object can be exactly superimposed on its mirror image. Left Ear: Chiral, because it isn’t superimposable on the right ear, its mirror image.
Are enantiomers chiral or achiral?
Enantiomers are always chiral, but diastereomers may or may not be chiral.
How to identify chirality centers?
In its simplest and most common case, a chirality center is characterised by an atom that has four different groups bonded to it in such a manner that it has a non-superimposable mirror image.
What is the difference between chiral and achiral?
Achiral objects are superimposable with their mirror images. For example, two pieces of paper are achiral. In contrast, chiral molecules, like our hands, are non superimposable mirror images of each other.
How do you identify chiral and achiral molecules?
In most cases, the easiest way to decide whether a molecule is chiral or achiral is to look for one or more stereocenters – with a few rare exceptions, the general rule is that molecules with at least one stereocenter are chiral, and molecules with no stereocenters are achiral.
Which compound is chiral or achiral?
Meaning of chiral and achiral compounds A molecule is classified as a chiral molecule if the mirror image of that molecule is not superimposable. The chiral molecule has two different stereoisomers, and these are known as enantiomers. Achiral molecules are those molecules that have superimposable mirror images.
What does achiral mean?
adjective. achi·ral ˌā-ˈkī-rəl. : of, relating to, or being a molecule that is superimposable on its mirror image : not chiral.
What is an example of an achiral compound?
Achirality in molecules also appears when a compound is divided into identical halves. For example, $1,2$dibromo cinnamic acid. In the above molecule carbon is attached to different atoms but the entire compound is divided into two equal halves therefore it is achiral compound.
What are chiral compounds?
A chiral compound can contain no improper axis of rotation (Sn), which includes planes of symmetry and inversion center. Chiral molecules are always dissymmetric (lacking Sn) but not always asymmetric (lacking all symmetry elements except the trivial identity). Asymmetric molecules are always chiral.
Are humans chiral or achiral?
For example, the left and right hands of a human are approximately mirror images of each other but are not their own mirror images, so they are chiral. In biology, 19 of the 20 natural amino acids are homochiral, being L-chiral (left-handed), while sugars are D-chiral (right-handed).
Is glass achiral?
Objects such as a chair, a drinking glass, and a fork have an internal plane of symmetry and hence are achiral.
Which protein is achiral?
Except for glycine, which is achiral, all the amino acids present in proteins. are chiral but racemic. have the L configuration at their α carbon. have the R configuration at their α carbon.
Do achiral compounds have handedness?
Achiral An object that lacks chirality; an object that has no handedness and is superposable on its mirror image. Plane of symmetry An imaginary plane passing through an object and dividing it such that one half is the mirror image of the other half.
Do all meso compounds have symmetry?
Meso compounds can exist in many different forms such as pentane, butane, heptane, and even cycloalkanes. Although two chiral carbons must be present, meso compounds can have many more. Notice that in every case a plane of symmetry is present.
What is meant by the chirality of a compound?
(i) Chirality is the property of a molecule to have non-super-imposable mirror image. These molecules contain one asymmetric carbon atom. e.g., Butan – 2- ol. (ii) CH3CH(Cl)CH2CH3 is more easily hydrolyzed due to the formation of more stable secondary carbocation.
What is achiral carbon in chemistry?
The carbon atom which is attached to the same substituents and lacks any chiral centre is called an achiral carbon atom. Achiral compounds are optically inactive in nature as they do not rotate the plane-polarized light.
What is meant by the word achiral?
Achiral – describes an object that does not have the property of handedness; the object can be superimposed on its mirror image.
Which amino acid is achiral?
All the amino acids are chiral except glycine. This means glycine is the only amino acid which contains two same groups and two different groups around the central carbon atom, that is, there are two hydrogen atoms , one amino group and one carboxyl group.
Is a molecule chiral or achiral?
Are achiral molecules symmetric or asymmetric?
Which molecule is achiral if it is superimposable?
What are examples of achiral compounds?
Achiral Compounds: The Basics
Imagine a mirror. Hold up your right hand in front of it, and you see a reflection of your left hand, right? That’s the basic idea of chirality in chemistry. It’s all about molecules and how they relate to their mirror images.
Achiral compounds are molecules that look exactly the same as their mirror images. They don’t have a stereoisomer that’s non-superimposable. Think of it like a pair of socks: you can turn them around, flip them over, and they’ll still be identical.
The Importance of Chirality
Chirality might seem like a small detail, but it’s actually a big deal in the world of organic chemistry. You see, many biological processes are highly stereospecific. This means they only work with one specific enantiomer – a molecule that’s a non-superimposable mirror image of another.
For instance, take thalidomide. This drug was once used to treat morning sickness. Unfortunately, one of its enantiomers caused severe birth defects. This is a stark reminder of how crucial chirality is in pharmaceuticals.
How to Tell if a Molecule is Achiral
To figure out if a molecule is achiral, there are a few tricks up our sleeve:
1. Check for a plane of symmetry: A plane of symmetry divides a molecule into two halves that are mirror images of each other. If you can find a plane of symmetry, the molecule is achiral.
2. Look for a chiral center: A chiral center is an atom (usually carbon) attached to four different groups. If a molecule has a chiral center, it’s likely chiral! However, there are exceptions, and some molecules with chiral centers can still be achiral.
3. Consider the molecule’s symmetry: If the molecule has multiple planes of symmetry or is highly symmetrical, it’s most likely achiral.
Common Examples of Achiral Compounds
Let’s look at some everyday examples of achiral compounds:
Water (H2O): The water molecule is bent, but it has a plane of symmetry.
Methane (CH4): Methane is a tetrahedral molecule with four identical hydrogen atoms attached to a central carbon atom. It has multiple planes of symmetry.
Carbon dioxide (CO2): Carbon dioxide is a linear molecule with two oxygen atoms on either side of the carbon atom. It also has multiple planes of symmetry.
Achiral Compounds in Action
Achiral compounds play a role in various fields, including:
Pharmaceuticals: As we’ve already discussed, chirality is important in pharmaceuticals. Some drugs are designed to be achiral to reduce the risk of side effects associated with specific enantiomers.
Materials Science: Achiral materials can have unique properties, like conductivity or optical transparency, which can be utilized for various applications.
Cosmetics:Achiral ingredients in cosmetics are often used to enhance texture and feel.
FAQs About Achiral Compounds
1. What is the difference between an achiral compound and a chiral compound?
Achiral compounds are molecules that look the same as their mirror images, while chiral compounds are molecules that are not superimposable on their mirror images.
2. Can a molecule with a chiral center be achiral?
Yes, a molecule with a chiral center can be achiral if it has other features that cancel out the chirality. For example, a molecule with two chiral centers can be achiral if they are enantiomers of each other.
3. How do I determine if a molecule is chiral or achiral?
The easiest way is to look for a plane of symmetry. If you can find one, the molecule is achiral. If not, it’s likely chiral.
4. Why is chirality important in pharmaceuticals?
Chirality is important in pharmaceuticals because many biological processes are stereospecific. This means they only work with one specific enantiomer of a drug.
5. Can an achiral compound become chiral?
Yes, an achiral compound can become chiral if you modify it in a way that breaks the symmetry. For example, adding a new functional group to an achiral molecule can introduce a chiral center.
Wrapping Up
Understanding achiral compounds and their role in chemistry is essential for anyone studying organic chemistry. Whether you’re in the lab or just trying to understand the world around you, knowing the difference between chiral and achiral molecules can make a world of difference.
See more here: Which Of The Following Compounds Is Achiral? | Achiral Compounds Are Those Which
Solved Part A Achiral compounds are those which
Question: Part A Achiral compounds are those which have the same formula but different structures. O have no “handedness. O e are non-superimposable. are a racemic mixture. have different mirror images. Chegg
4.2: Chiral and Achiral Molecules – Chemistry LibreTexts
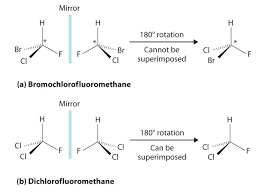
Whether a molecule is chiral or achiral depends upon a certain set of overlapping conditions. Figure 1 shows an example of two molecules, chiral and achiral, Chemistry LibreTexts
Chemistry 19 – Exam 3 Flashcards | Quizlet
Achiral compounds are those which _____. a) are nonsuperimposable b) have the same formula but different structures c) have no “handedness” d) have a carbon attached to four different atoms e) have different mirror Quizlet
Chiral and Achiral Molecules – Organic Chemistry
What are chiral and achiral molecules? A molecule is considered chiral if there exists another molecule that is of identical composition but which is arranged in a non-superposable mirror image. Socratic
Chiral vs achiral (video) | Stereochemistry | Khan Academy
A molecule that is meso has two or more chiral centres but, overall, the molecule is achiral because it can be superimposed on its mirror image. Therefore, meso compounds have no optical activity. Furthermore, meso compounds always have an internal Khan Academy
Chirality and Optical Activity – Division of Chemical
Compounds that contain a single stereo-center are always chiral. Some compounds that contain two or more stereocenters are achiral because of the symmetry of the relationship between the stereocenters. The prefix Division of Chemical Education
Explain three examples of chiral and Achiral
Achiral compound. Achiral molecules have superimposable mirror images. They lack chiral centers and the center of a compound that is attached to similar types of the substituent is known as the achiral BYJU’S
exam chem 3 quiz 8 Flashcards | Quizlet
Achiral compounds are those which a. have no “handedness” b. have different mirror images c. are a pair of enantiomers d. have D and L isomers Quizlet
QUIZ 4, 5, & 6 Flashcards | Quizlet
A chemical reaction has reached equilibrium when ________. all products have been removed from the reaction mixture. the catalyst has been used up. the rate of the quizlet.com
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Chiral Vs Achiral Molecules – Chirality Carbon Centers, Stereoisomers, Enantiomers, \U0026 Meso Compounds
Chiral And Achiral Molecules – Allenes And Alkenes
How To Find Chiral Centers \U0026 The Difference Between Chiral Vs Achiral Molecules | Organic Chemistry
Chirality|Basic Concept Explained
How To Determine If A Molecule Is Chiral Or Achiral? With A Step By Step Chart And Examples!
Link to this article: achiral compounds are those which.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/