Is glucose soluble in water or not?
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water.
Is glucose likely to dissolve in water?
Glucose forms white or colorless solids that are highly soluble in water and acetic acid but poorly soluble in methanol and ethanol.
Does glucose dissolve well in water?
Why do you think glucose molecules dissolve well in water? Glucose has many areas where oxygen is bonded to hydrogen. These O–H bonds are polar. Polar water molecules and the polar areas of glucose molecules are attracted to each other, causing the corn syrup to dissolve.
Is sugar soluble in water yes or no?
It also takes energy to break the hydrogen bonds in water that must be disrupted to insert one of these sucrose molecules into solution. Sugar dissolves in water because energy is given off when the slightly polar sucrose molecules form intermolecular bonds with the polar water molecules.
Why does glucose not break apart in water?
Answer and Explanation: The sugar molecule is considered a nonelectrolyte and it does not dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. It is soluble in water due to the hydroxyl groups present in the structure. The hydroxyl groups can interact with water by hydrogen bonding.
Is glucose a solute in water?
For example, in a solution of the sugar glucose in water, glucose molecules are the solute and water molecules are the solvent. In beer, which is typically 2–4% ethanol, ethanol is the primary solute and water is the solvent.
How much glucose can dissolve in water?
For example, the solubility of glucose at 25 °C is 91 g glucose per 100 mL of water, and the solubility of glucose at 50 °C is 244 g glucose per 100 mL of water.
What is a glucose dissolved in water called?
When sugar is dissolved in water, the solution obtained is called. aqueous solution.
Which is most soluble in water?
When applying energy to the polar sucrose molecules, there is a formation of intermolecular bonds with the polar water molecules. And that intermolecular bonds are very weak and it gives the energy to derange the structure of both pure solvent and the solute. Therefore, sugar is most soluble in water.
Does glucose mix with water?
A solution of glucose in water is a homogeneous mixture.
Why is my sugar not dissolving in water?
Sugar crystals do not dissolve easily in ice cold water, because the low temperature slows down the process of diffusion. The solvent has low kinetic energy and therefore cannot move faster to surround the sugar crystals.
How to dissolve sugar in water?
Sugar dissolves faster in hot water than it does in cold water because hot water has more energy than cold water. When water is heated, the molecules gain energy and, thus, move faster. As they move faster, they come in contact with the sugar more often, causing it to dissolve faster.
What happens if you mix sugar and water?
When you mix sugar and water, the sugar will dissolve into the water and will create a solution. The solution will be homogeneous because the sugar is fully dissolved, and you can no longer see it. Water is the solvent that dissolves the sugar, and the sugar is the solute.
Why is glucose so soluble in water?
The reason glucose dissolves readily in water is because it has lots of polar hydroxyl groups which can hydrogen-bond with water molecules. Hydrogen bonds are very important intermolecular forces which determine the shape of molecules like DNA, proteins and cellulose.
Is glucose or sucrose soluble in water?
Glucose contain 5 – OH groups and sucrose contain eight – OH groups, because of this they form intermolecular hydrogen bonding, so they are soluble in water.
Is glucose in water a true solution?
Reason (R): True solution is a homogeneous mixture that contains small solute particles that are dissolved throughout the solvent.
Why do sugars dissolve easily in water?
Sucrose is a polar molecule. The polar water molecules attract the negative and positive areas on the polar sucrose molecules which makes sucrose dissolve in water. A nonpolar substance like mineral oil does not dissolve a polar substance like sucrose.
Is glycogen insoluble in water?
Glycogen is insoluble because it doesn’t have enough free polar groups to participate in hydrogen bonding with water. This is because most of the polar OH groups in glycogen hydrogen bond with other groups within the molecule leaving few groups available to participate in bonding with water.
Is glucose readily soluble in water?
Glucose’s six oxygen atoms increase its ability to dissolve in water, In particular, since five of those oxygen atoms are found in the form of alcohol groups, which allows it to readily form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and makes it very water-soluble, glucose dissolves quite readily in water.
Does glucose dissolve or does not dissolve in water?
Glucose dissolves in water because polar water molecules attach to the glucose molecules. The many O-H (hydroxyl- ) groups in glucose are attracted to the water molecules by dipole-dipole forces. The strength of these forces can be greater than the glucose -glucose interactions.
Is glucose a sugar?
Glucose comes from the Greek word for “sweet.” It’s a type of sugar you get from foods you eat, and your body uses it for energy. As it travels through your bloodstream to your cells, it’s called blood glucose or blood sugar.
What is glucose solution in water?
10% w/w glucose solution means 10 g glucose present in 100 g of solution which contains 90 g of water. Molality is the number of moles of glucose present in 1 kg of water. Molar mass of glucose (C6H12O6) = 6×12+12×1+6×16=180gmol−1.
Is glucose soluble in blood?
Our bloodstream is key to getting the glucose and glycogen into our body’s tissues to be used as energy. Glucose begins to dissolve as it flows throughout our blood and the circulatory system, reaching the necessary tissues. This is why the amount of glucose circulating throughout the body is called blood glucose.
Is glucose hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Glucose has hydrophilic nature. Therefore, cell membranes act as barriers to most molecules. For water molecules and a few other small molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, the lipid bilayer is permeable.
Does glucose mix with water?
A solution of glucose in water is a homogeneous mixture.
Why glucose or sucrose are soluble in water?
Glucose contain 5 – OH groups and sucrose contain eight – OH groups, because of this they form intermolecular hydrogen bonding, so they are soluble in water.
How much glucose can dissolve in water?
For example, the solubility of glucose at 25 °C is 91 g glucose per 100 mL of water, and the solubility of glucose at 50 °C is 244 g glucose per 100 mL of water.
Why does sugar dissolve in water?
Is glucose soluble in water?
What is the solubility of glucose?
Is D-glucose soluble in water?
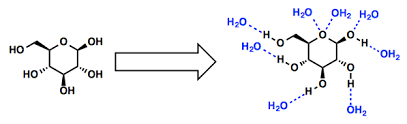
Why is Glucose Soluble in Water?
The key to understanding why glucose dissolves in water lies in its structure and how it interacts with water molecules.
Glucose is a sugar molecule, with the chemical formula C6H12O6. It’s a carbohydrate, which means it’s made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
Now, let’s look at the structure of glucose. Imagine a bunch of atoms linked together like a chain. Glucose is a ring-shaped molecule. This ring is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. At the edges of the ring, there are hydroxyl groups (OH).
These hydroxyl groups are the key to glucose’s solubility in water. They are polar. This means that one end of the hydroxyl group has a slightly positive charge while the other end has a slightly negative charge.
Water, you know, is also a polar molecule. It has a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end. This creates a dipole moment in the water molecule.
So, when you put glucose in water, the polar hydroxyl groups of glucose form hydrogen bonds with the polar water molecules. These hydrogen bonds are weak attractive forces, but they are strong enough to overcome the attraction between glucose molecules.
Essentially, the water molecules surround the glucose molecules, breaking them apart and allowing them to dissolve.
The Process of Dissolution
Imagine a sugar cube dropping into a glass of water. The sugar cube is a solid, but as it dissolves, it breaks down into individual glucose molecules. These molecules then disperse throughout the water, creating a homogeneous mixture.
This means that the glucose molecules are evenly distributed throughout the water, and you can’t distinguish them from the water molecules.
Factors Affecting Glucose Solubility
While glucose is generally soluble in water, there are some factors that can affect its solubility:
Temperature: Increasing the temperature of the water increases the solubility of glucose. This is because the higher temperature provides more energy to break the bonds between glucose molecules and to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Concentration: The solubility of glucose is limited. This means that there’s a certain point where no more glucose can dissolve in water. This point is called the saturation point. Once the saturation point is reached, any additional glucose will simply settle to the bottom of the container.
pH: The solubility of glucose is slightly affected by pH. A slightly acidic or slightly basic pH can decrease its solubility, but it’s generally not a significant factor.
Glucose in our Bodies
Glucose is a vital nutrient for our bodies. It’s the primary source of energy for our cells.
When we eat food containing carbohydrates, our bodies break down these carbohydrates into glucose. This glucose is then absorbed into our bloodstream and transported to our cells.
Inside our cells, glucose is used in a process called cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
FAQs
Q: What is the solubility of glucose in water?
A: The solubility of glucose in water at room temperature is about 90 grams per 100 milliliters. This means that you can dissolve about 90 grams of glucose in 100 milliliters of water.
Q: Is glucose soluble in other liquids besides water?
A: Glucose is also soluble in other polar solvents like ethanol and methanol. However, it is not soluble in non-polar solvents like oil or gasoline.
Q: Why is glucose important for our bodies?
A: Glucose is essential for our bodies because it’s the primary source of energy for our cells. Without glucose, our cells would not be able to function properly.
Q: Can I make glucose soluble in water?
A: Glucose is already soluble in water, but you can increase its solubility by heating the water. Increasing the temperature provides more energy to break the bonds between glucose molecules.
Q: What are some examples of foods that contain glucose?
A: Glucose is found in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
Let me know if you have any more questions about glucose and its solubility!
See more here: Is Glucose Likely To Dissolve In Water? | Is Glucose Soluble In Water
The Comprehensive Guide to Glucose Solubility: A Deep Dive
The solubility of glucose in water is approximately 900 g/L at 25°C, which means that 900 grams of glucose can be dissolved in one liter of water at this temperature. This high solubility is due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between the glucose techiescience.com
The Solubility of Glucose: A Comprehensive Guide
Glucose, a monosaccharide and the primary source of energy for many organisms, has a solubility of approximately 1.0 g/mL in water at room temperature. techiescience.com
Glucose C6H12O6 – Chemical Formula, Structure,
Glucose is a simple sugar with the formula C6H12O6 that is water-soluble and sweet to taste. It is a monosaccharide with an aldehyde group and can be prepared from sucrose BYJU’S
4.4 Solubility – Chemistry LibreTexts
Sugars often lack charged groups, but as we discussed in our ‘thought experiment’ with glucose, they are quite water-soluble due to the presence of multiple hydroxyl groups. Some biomolecules, in contrast, Chemistry LibreTexts
Chapter 9.2: Solubility and Structure – Chemistry LibreTexts
Consequently, glucose is very soluble in water (91 g/120 mL of water) but essentially insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene. The structure of one isomer of glucose is shown here. Chemistry LibreTexts
(PDF) Glucose: Properties and analysis
Solubility of glucose. Mechanisms of base-and acid-catalyzed mutarotation reactions. Example of sugar phosphate metabolic intermediate (D-glucose 6-phosphate). Products of reaction of D ResearchGate
Why Does Water Dissolve Sugar? – American Chemical Society
Learn how the polar characteristics of water and sugar molecules attract each other and make sugar dissolve in water. See the activity and materials to observe American Chemical Society
Solubility – Division of Chemical Education, Purdue
Learn why some solids dissolve in water and how to predict solubility based on solubility rules. Glucose is a molecular solid that dissolves in water because of hydrogen bonding. Division of Chemical Education
Molecular structure of glucose (video) | Khan Academy
Learn about the chemical formula, structure and properties of glucose, a monosaccharide that is the main source of energy for living organisms. See how glucose can form linear and ring shapes, and how it is soluble in water. Khan Academy
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Pop Up Science: Sugar And Water
How Solubility And Dissolving Work
Sugar Dissolving
Equation For Glucose Dissolving In Water (C6H12O6 + Water)
Salt And Sugar Are Soluble In Water But Sand Is Not | Solutions | Chemistry
Link to this article: is glucose soluble in water.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/