Can NMO be detected in a blood test?
A health care provider might test the blood for the aquaporin-4-immunoglobulin G, also called AQP4-IgG antibody. This test shows a difference between NMO and MS . This test helps in making an early diagnosis of NMO .
What is a neuromyelitis spectrum profile blood test?
Mitogen’s Neuromyelitis Spectrum assay is an autoimmune diagnostic test that detects autoantibodies to Aquaporin 4 & Anti-Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoproteins (MOG). Aquaporin-4, also known as AQP4 or NMO-IgG, is a water channel membrane protein that conducts water through the cell membrane.
What is NMO positive?
NMO is an autoimmune condition. This means the body’s immune system reacts abnormally and attacks healthy tissues, causing the symptoms of NMO. NMO is usually not inherited, but some people with NMO may have a history of autoimmune disorders in the family and may have another autoimmune condition themselves.
What is anti aquaporin-4 blood test?
Anti-AQP4 antibody is clinically useful not only for differentiating between NMO and MS with optic nerve and spinal cord presentations, but also for its predictive value following acute attacks of myelitis.
What is the best test for NMO?
Blood tests. One of the most important tools for healthcare providers to diagnose NMO is testing your blood for AQP4 or MOG antibodies. While blood testing can’t always confirm NMO — because about 13.5% of cases don’t involve identifiable antibodies — it’s still useful for diagnosing this condition.
What is the anti NMO antibody test?
The NMO antibody test measures the presence and quantity of AQP4 antibodies in your blood serum. For this purpose, you need to provide your blood specimen through the process of venepuncture.
What is NMO and MOG antibody test?
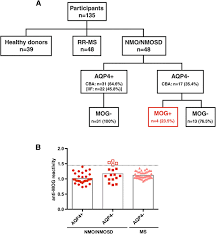
The presence of NMO & MOG antibodies is diagnostic of NMO and related spectral disorders. 80% of NMO patients test positive for NMO antibodies while 20% of patients may test negative, but will test positive for MOG antibodies. This test helps to diagnose and distinguish this disorder from multiple sclerosis.
What are NMO antibodies?
Also known as: NMO; AqP4; Aquaporin 4. Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) is the major autoantigen in neuromyelitis optica (NMO, or Devic’s disease). Antibodies to AQP4 are found in >80% of NMO patients and around 50% of patients with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis.
Is ANA positive in NMO?
Neuromyelitis optica (NMOSD) patients often have antinuclear antibodies (ANAs). ANA-positive NMOSD patients have higher NMO-IgG titers. ANA-positive NMOSD patients more often have non-organ specific autoantibodies. The presence of ANA does not alter disease course in NMOSD patients.
How do I know if I have NMO?
How is neuromyelitis optica diagnosed? Your healthcare provider may do a variety of tests if they suspect NMO, such as: MRI scan of your brain and spinal cord. Tests to check on how well your optic nerves are working.
What does a positive mog antibody mean?
Antibodies to MOG cause the myelin sheath to fall off, this is known as demyelination. Demyelination means that messages cannot pass along the nerve effectively and these messages may slow down or stop completely. This in turn can cause neurological (brain and nervous system) symptoms.
What is the blood test for neuromyelitis optica?
Quest also offers the NMO Spectrum Evaluation, which begins with AQP4 testing and reflexes to MOG testing if AQP4 is negative (Table 2). Includes AQP4 antibody; if AQP4 is positive, reflex to titer; if AQP4 is negative, reflex to MOG antibody; if MOG is positive, reflex to titer.
What is anti neuronal antibodies test?
This test detects IgG antineuronal antibodies to Hu, Ri, Yo and Tr (DNER) antigens. Antineuronal antibodies serve as markers that aid in discriminating between a true paraneoplastic neurological disorder (PND) and other inflammatory disorders of the nervous system.
What is the normal range for aquaporin-4 antibody?
Remember the range is from 2.1 to 71.7. The median end titer was 1,000. So these are robust, generally, titers of antibody. And the median age of aquaporin-4 IgG seropositive patients was 56 years.
What is the blood test for NMO MOG?
NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA ANTIBODY PANEL (National) Test Overview : This panel includes antibodies against anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) and Aquaporin4 (AQP4) and is used to help establish the diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and related disorders.
What are NMO IgG autoantibodies?
Clinical Significance Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) (NMO-IgG) Antibody with Reflex to Titer, Serum – NMO (neuromyelitis optica, Devic disease) is an immune- mediated chronic inflammatory disease that predominantly affects the optic nerve and spinal cord and presents with optic neuritis (ON) and myelitis.
What is the sample for the NMO test?
The sample for this test is Blood or CSF. Blood is collected by inserting a small needle into vein of the arm. A small amount of blood is then collected in a vacutainer. There may be a little pain due to needle prick.
What is the other name for NMO test?
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO), also known as Devic’s disease or Devic’s syndrome, is an autoimmune, inflammatory disorder in which a person’s own immune system preferentially attacks the optic nerves and spinal cord producing optic neuritis and myelitis [1].
What is the biomarker of NMOSD?
Serological VEGF, MPIF-1 and NrCAM were positively associated with AQP4-IgG titer in NMOSD patients. IL-17B may be a key biomarker of NMOSD and MS. Increased expression of EGF in NMOSD patients contribute to the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier.
What are the antibodies for NMOSD?
NMOSD primarily targets the optic nerves, brainstem, and spinal cord, presenting a unique set of challenges for diagnosis and management. This disorder, comprising six syndromes, is intricately linked to aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G antibodies (AQP4-IgG), necessitating serologic testing for accurate evaluations.
What is the difference between NMO and MOG antibody?
But unlike NMO, which generally targets a water channel called aquaporin-4 on astrocytes, the immune dysfunction in MOG targets the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein on the outermost myelin membranes surrounding the optic nerves, spinal cord and brain.
How to diagnose NMOSD?
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to look for damage to your optic nerves, spinal cord and brain. A spinal tap (lumbar puncture) to examine the fluid surrounding your spinal cord and brain for signs of NMOSD. Eye tests to check for blurry vision or loss of color perception.
How do you test for MOG antibody?
There are blood tests that can test for MOG antibodies. Only cell-based assays are considered reliable for the diagnosis of MOGAD because of the improved specificity over older ELISA tests.
What is a mog antibody?
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody disease (MOGAD) is a neurological, immune-mediated demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system that causes inflammation and potential damage in the optic nerve, spinal cord, brain and/or brainstem.
What is NMO autoimmune disease?
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is a central nervous system disorder that causes inflammation in nerves of the eye and the spinal cord. NMO is also called neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) and Devic disease. It occurs when the body’s immune system reacts against its own cells.
What is the aquaporin-4 antibody test?
Abstract. Antibodies to aquaporin-4 (called NMO-IgG or AQP4-Ab) constitute a sensitive and highly specific serum marker of neuromyelitis optica (NMO) that can facilitate the differential diagnosis of NMO and classic multiple sclerosis.
How do I know if I have NMO?
How is neuromyelitis optica diagnosed? Your healthcare provider may do a variety of tests if they suspect NMO, such as: MRI scan of your brain and spinal cord. Tests to check on how well your optic nerves are working.
Is ANA positive in NMO?
Neuromyelitis optica (NMOSD) patients often have antinuclear antibodies (ANAs). ANA-positive NMOSD patients have higher NMO-IgG titers. ANA-positive NMOSD patients more often have non-organ specific autoantibodies. The presence of ANA does not alter disease course in NMOSD patients.
Can NMO go away on its own?
It is not known if the body can heal damage to the spinal cord, optic nerves or brain caused by NMO. It is possible that by preventing relapses, these tissues may repair themselves over time. However, it is also possible that tissue caused by NMO may be irreversible.
Can you see an NMO on MRI?
Spinal cord lesions extending over 3 or more vertebral segments are the typical MRI finding in NMO. Shorter MRI lesions can be found very early during relapse or in residual atrophic stages. Some of the lesions may appear hypointense on corresponding T1-weighted images which reflects sever inflammation with necrosis.
What is neuromyelitis optica (NMO)?
What are blood tests for NMOSD?
How does a neurologist test for NMO?
How do I know if I have NMO or MS?
So, you’ve heard the term “anti-NMO antibody blood test” and you’re probably wondering what it’s all about, right? Let’s dive in and break it down. This test is a powerful tool used to help doctors diagnose a specific autoimmune disorder called neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD).
It’s like a detective tool, helping doctors pinpoint the culprit behind certain symptoms you might be experiencing. But, before we get into the nitty-gritty, let’s get a handle on what NMOSD is all about.
Understanding NMOSD
NMOSD is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body’s immune system, which is supposed to protect you from invaders like bacteria and viruses, starts attacking your own tissues. In the case of NMOSD, the immune system targets the myelin sheath, a protective coating around nerve fibers in your brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. This attack can cause inflammation and damage, leading to a range of symptoms like:
Vision problems: Blurred vision, double vision, and even blindness
Muscle weakness: Difficulty walking, controlling your limbs, and even breathing
Sensory problems: Numbness, tingling, or pain
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness
Bowel and bladder dysfunction: Difficulty controlling bowel movements or urination
The symptoms can vary from person to person and can come on suddenly, which can be pretty scary. This is where the anti-NMO antibody blood test comes into play.
The Anti-NMO Antibody Blood Test: Your Body’s Clues
This test looks for the presence of anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibodies in your blood. These antibodies are the key players in NMOSD. They’re like little soldiers in your blood that mistakenly attack the AQP4 protein, which is a vital component of the myelin sheath.
When the test detects these antibodies, it’s a strong indicator that you might have NMOSD. However, it’s important to note that not everyone with NMOSD will have these antibodies. Some people might have a different type of antibody, like anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibody, or no detectable antibody at all.
Why This Test Is So Important
The anti-NMO antibody blood test is crucial for several reasons:
1. Diagnosis: It helps doctors confirm or rule out NMOSD, especially when symptoms overlap with other conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS).
2. Treatment: The presence of these antibodies can influence treatment decisions. Doctors might recommend stronger medications or a different approach based on the test results.
3. Prognosis: The presence of these antibodies can also give doctors clues about the long-term course of the disease and how likely it is to return.
Getting the Test: What to Expect
If your doctor suspects NMOSD, they will likely order an anti-NMO antibody blood test. The procedure itself is simple:
1. Blood Draw: A healthcare professional will take a small sample of your blood.
2. Lab Analysis: The blood sample will be sent to a lab for analysis.
3. Results: The results usually take a few days to a week.
The Role of the Neurologist
It’s important to understand that the anti-NMO antibody blood test is just one piece of the puzzle. Your doctor will likely consider your symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic tests, like MRI scans, to reach a definitive diagnosis. They’ll also need to rule out other possible conditions that might cause similar symptoms.
What to Do If You Have Questions
If you have any questions about the anti-NMO antibody blood test or NMOSD, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor. They can provide personalized information and answer your concerns.
Now, let’s address some common questions people have about this test:
FAQs about the Anti-NMO Antibody Blood Test
1. What are the symptoms of NMOSD?
As we mentioned before, NMOSD can present with a variety of symptoms, including:
Vision problems: Blurred vision, double vision, and even blindness.
Muscle weakness: Difficulty walking, controlling your limbs, and even breathing.
Sensory problems: Numbness, tingling, or pain.
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness.
Bowel and bladder dysfunction: Difficulty controlling bowel movements or urination.
2. How accurate is the anti-NMO antibody blood test?
The accuracy of the anti-NMO antibody blood test depends on several factors, but it’s generally considered very accurate. If the test is positive, it strongly suggests you have NMOSD. However, it’s not always foolproof.
3. What happens if the test is negative?
A negative test doesn’t necessarily mean you don’t have NMOSD. You might have a different type of antibody, like anti-MOG antibody, or the antibodies might not be detectable in your blood at that particular time.
4. Does the test require any special preparation?
No, the anti-NMO antibody blood test doesn’t usually require any special preparation.
5. What are the risks associated with the test?
The anti-NMO antibody blood test is generally safe and involves minimal risks, similar to a routine blood draw. You might experience a slight bruise or discomfort at the puncture site.
6. How often do I need to have the test?
Your doctor will advise you on the frequency of testing based on your individual needs. It might be recommended to repeat the test if your symptoms change or if there are concerns about the disease’s progression.
7. What happens after the test?
Once you receive the test results, your doctor will discuss the findings with you. They’ll help you understand what the results mean and discuss the next steps in your care.
8. What are the treatment options for NMOSD?
Treatment for NMOSD typically involves medications to suppress the immune system and prevent further attacks on the nervous system. The specific treatment will depend on the severity of your symptoms and the underlying cause of the disease.
9. Is there anything I can do to prevent NMOSD?
There’s no known way to prevent NMOSD, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the disease and prevent complications.
10. Where can I find more information about NMOSD?
There are several resources available for more information about NMOSD, including the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the Guillain-Barré Syndrome Foundation, and the Neuromyelitis Optica Foundation.
The anti-NMO antibody blood test is a valuable tool for understanding and managing NMOSD. It can help provide a definitive diagnosis, guide treatment decisions, and offer valuable information about the long-term course of the disease. Remember, if you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor. They’re there to help you understand your condition and make informed decisions about your care.
See more here: What Is A Neuromyelitis Spectrum Profile Blood Test? | Anti Nmo Antibody Blood Test
Getting a Blood Test for NMO Can Help with Diagnosis
What blood tests are done for NMOSD? Your doctor will order various blood tests to diagnose NMOSD. The 2 most common blood tests include: 1,2. AQP4 antibody neuromyelitis-optica.net
Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO): What It Is, Symptoms
Blood tests. One of the most important tools for healthcare providers to diagnose NMO is testing your blood for AQP4 or MOG antibodies. While blood testing can’t always confirm NMO — because about 13.5% of Cleveland Clinic
004210: Neuromyelitis Optica, IgG Autoantibodies | Labcorp
Establishing the diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and related disorders, including relapsing transverse myelitis or relapsing optic neuritis. Distinguishing NMO and NMO Labcorp
Update on the diagnosis and treatment of neuromyelits optica
A key focus is on differentiating NMOSD from MS and from myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated encephalomyelitis (MOG-EM; also National Center for Biotechnology Information
NMO-Specific Antibodies: Important Information to Know
What is AQP4? AQP4 stands for aquaporin-4. It is a protein on the outside of certain brain cells. It controls water balance. Specifically, it controls how water moves in and out of neuromyelitis-optica.net
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD): Clinical
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD; previously known as Devic disease or neuromyelitis optica [NMO]) is an inflammatory disorder of the central UpToDate
Neuromyelitis Optica: Mayo Clinic Blood Test Supports Clinical
All three patients test posi-tive for the neuromyelitis optica (NMO) antibody. NMO is a demyelinating disease that affects the optic nerves and the spinal cord. It can lead to Mayo Clinic
NMOFS – Overview: Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO)/Aquaporin-4
Diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica (NMO) Distinguishing NMOSD from multiple sclerosis early in the course of disease. Reflex Tests. Testing Algorithm. Mayo Clinic Laboratories
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD)
Blood tests to measure an IgG antibody specific for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (aquaporin-4 antibody [also known as NMO-IgG]) may be done to MDS Manuals
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
How Do I Request The Nmo Igg Antibody Test?
Aqp4-Ab
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder, Causes, Signs And Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment.
Medical Stories – Nmosd: Blindsided Within
Immunopathology Of Neuromyelitis Optica/Devic’S Disease
Link to this article: anti nmo antibody blood test.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/