When can diseconomies of scale occur?
Diseconomies of scale happen when a company or business grows so large that the costs per unit increase. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function for a firm.
When diseconomies of scale occur, the long run?
A firm is said to experience diseconomies of scale when long-run average cost increases as the firm expands its output. Constant returns to scale occur when long-run average cost stays the same over an output range.
When diseconomies of scale at the firm level occur?
In economics, the term diseconomies of scale describes the phenomenon that occurs when a firm experiences increasing marginal costs per additional unit of output. It is the opposite of economies of scale.
What may cause economies or diseconomies of scale?
Economies of scale occur in a business when costs per unit of a product decreases as the business expands. Diseconomies of scale happen when production costs increase per product as the business expands. Companies must balance the economies of scale vs. diseconomies of scale while they are looking to grow.
When can diseconomies of scale occur in Quizlet?
Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm increases output and this leads to an increase in average cost of production.
In which time does economies of scale occur?
Economies of scale arise when producers’ average total cost falls as output increases (Mankiw, 1998). In education, this suggests that larger schools and districts may face a lower per-pupil cost.
Can diseconomies of scale occur in the short run?
Answer and Explanation: Diseconomies of scale occur in the long-run but not the short-run. This is because some inputs are fixed in the short-run and the cause of the increasing average total cost in the short-run is likely due to diminishing returns from increasing variable inputs.
Why do economies and diseconomies of scale occur in the long run?
Economies of scale exist when long run average total cost decreases as output increases, diseconomies of scale occur when long run average total cost increases as output increases, and constant returns to scale occur when costs do not change as output increases.
Are economies of scale only in the long run?
The economies of scale curve is a long-run average cost curve, because it allows all factors of production to change. Short-run average cost curves assume the existence of fixed costs, and only variable costs were allowed to change.
What are the three types of diseconomies of scale?
Diseconomies of scale are the opposite of economies of scale, which is when the price to produce a single unit decreases in response to increased output. There are internal types of diseconomies of scale, like technical, organizational and financial diseconomies, and external diseconomies of scale, like infrastructure.
When economies of scale occur when a company is operating?
Economies of scale are cost advantages companies experience when production becomes efficient, as costs can be spread over a larger amount of goods. A business’s size is related to whether it can achieve an economy of scale—larger companies will have more cost savings and higher production levels.
What are the external causes of diseconomies of scale?
Sources of Diseconomies of Scale The scarcity of electricity, water, finance, and other factors of production raises the price. Local roads become congested and so the transportation cost begins to rise. Local labour becomes scarce and firms have to offer higher wages to attract new workers.
What are the factors causing economies of scale?
These could include using more efficient production techniques, hiring more skilled workers, or investing in new technology. External economies of scale can arise from industry-wide investments in infrastructure, research and development, or marketing, which can benefit all companies in the industry.
What is an important cause of internal diseconomies of scale?
Answer: The main cause of the internal diseconomies is the lack of efficient or skilled management. When a firm expands beyond a certain limit, it becomes difficult for the manager to manage it efficiently or to co-ordinate the process of production.
When and why do diseconomies of scale take place?
Diseconomies of scale occur when a business grows so large that the costs per unit increase. As output rises, it is not inevitable that unit costs will fall. Sometimes a business can get too big! Diseconomies of scale occur for several reasons, but all as a result of the difficulties of managing a larger workforce.
When diseconomies of scale begin to outweigh the economies of scale?
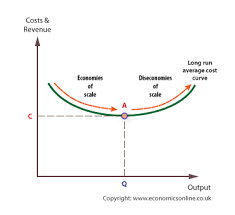
Long run cost curves look at the impact of factor prices on a firm; as the firm increases the scale of production, economies of scale lead to lower average costs per unit. At some point, the minimum efficient scale, diseconomies of scale start to outweigh economies of scale and average costs per unit begin to rise.
How diseconomies of scale arise due to increasing returns?
Diseconomies of scale arise when the expansion of a firm’s production leads to an increase in the average cost per unit. Typically, this occurs when production becomes too large, and inefficiencies emerge due to problems with coordination, communication, or logistics.
What is the difference between economies of scale and diseconomies of scale?
Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing.
What are the advantages of diseconomies of scale?
Some advantages of diseconomies of scale are as follows: The business will tend to make a better effort to devise ways and means to control cost and at the same time increase production through better technology, innovation, planning.
Does economies of scale occur in the short run?
Economies of scale exist when the average cost decreases as output increases. Because firms are constrained by their capital size, in the short-run, however, economies of scale are only evaluated in the long-run, when the firm has the ability to select their capital size.
What time period do economies of scale occur?
Economies of scale can be realized by a firm at any stage of the production process.
What are the three diseconomies of scale?
There are three main reasons for diseconomies of scale: managerial diseconomies of scale, communication failure, and motivational diseconomies of scale. There are two main types of diseconomies of scale: internal diseconomies of scale and external diseconomies of scale.
Why do economies of scale occur?
Economies of scale are cost advantages that can occur when a company increases their scale of production and becomes more efficient, resulting in a decreased cost-per-unit. This is because the cost of production (including fixed and variable costs) is spread over more units of production.
What is the long run period?
The long run refers to a period of time where all factors of production and costs are variable. Over the long run, a firm will search for the production technology that allows it to produce the desired level of output at the lowest cost.
What is the 0.6 rule?
A crude estimate is that if the capital cost for a given sized piece of equipment is known, changing the size will change the capital cost by the 0.6 power of the capacity ratio (the point six to the power rule).
Do economies of scale exist whenever?
Economies of scale – exist whenever long-run average costs decline as output increases. Economies of scope – exists when the total cost of producing two products within the same firm is lower than when the products are produced by separate firms.
Under which conditions might diseconomies of scale result?
Diseconomies of scale may result from several factors, including communication breakdown, lack of motivation, lack of coordination, and loss of focus by the management and employees.
What is an example of diseconomies of scale in real life?
Examples of internal diseconomies of scale include: poor coordination, poor communication, poor control, demotivation of workers, complacency, alienation of workforce and bureaucracy.
What are the two possible diseconomies of scale?
There are two main categories of diseconomies of scale: internal and external. While internal diseconomies of scale result from factors within the company’s control, external diseconomies of scale occur due to factors outside of a company’s influence.
What are diseconomies of scale?
When does diseconomy of scale occur?
What are internal diseconomies of scale?
What does decreasing returns to scale mean?
Imagine this: You’re running a pizza place. You start small, maybe just you and a couple of friends making pizzas in your basement. You’re super efficient, everyone knows their role, and you’re churning out pizzas like crazy. As your business grows, you need more space, more ovens, more staff. Things are still good, you’re getting those economies of scale, you know, where producing more costs less per unit.
But then…
You keep growing, you hire more people, and now it’s getting crowded. You have to hire a manager to keep everyone in line, and suddenly communication gets messed up. Maybe you’re making so many pizzas that your ovens can’t keep up, and you’re losing time and money trying to catch up. This, my friend, is where diseconomies of scale kick in.
Diseconomies of scale happen when increasing production actually leads to higher costs per unit. It’s like the opposite of economies of scale. It’s when growth becomes a burden, not a blessing.
So, when does this diseconomies of scale thing happen?
There are a few key reasons:
Management issues: As your business gets bigger, it becomes harder to manage. You might have too many layers of management, leading to slow decision-making and communication breakdowns.
Coordination problems: When you have a lot of people working together, it’s harder to coordinate everyone’s efforts. This can lead to inefficiencies and wasted resources.
Increased bureaucracy: As your business grows, you might need to implement more rules and regulations. This can slow down decision-making and make it harder for your employees to be creative.
Difficult to find and retain skilled labor: As you grow, you’ll need to hire more people. But finding and keeping qualified employees can be a challenge, especially if you’re in a competitive industry.
Diminishing returns on investments: At some point, your investments might start to yield diminishing returns. Think about that extra oven you bought. If you’re already running your ovens at full capacity, that extra oven is just going to sit there, costing you money.
Let’s talk about some examples
A car manufacturer: Imagine a car manufacturer that keeps building more factories to increase production. But if they don’t have the right management in place to handle all those factories, they might end up with coordination problems and higher costs.
A tech company: A tech company might hire more developers to work on a new project. But if they don’t have the right systems in place for communication and collaboration, the project might become bogged down.
A restaurant: A restaurant might expand its menu to attract more customers. But if the kitchen staff isn’t prepared for the extra workload, the quality of the food might suffer, and customers might be disappointed.
Here’s what you can do to avoid diseconomies of scale:
Invest in good management: Make sure you have strong leaders who can motivate and guide your employees.
Optimize your processes: Streamline your operations to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
Embrace technology: Use technology to improve communication and collaboration.
Focus on quality: Don’t sacrifice quality for quantity.
Be adaptable: Be willing to change your approach as your business grows.
It’s all about finding that sweet spot, that perfect balance between growth and efficiency. You want to grow your business, but you don’t want to lose your competitive edge by getting too big and unwieldy.
So, remember, growth is good, but too much growth can be a bad thing. Keep an eye on those diseconomies of scale and you’ll be well on your way to building a successful business.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between economies of scale and diseconomies of scale?
A: Economies of scale happen when increasing production leads to lower costs per unit. Diseconomies of scale happen when increasing production leads to higher costs per unit.
Q: How can I tell if my business is experiencing diseconomies of scale?
A: Look for signs like declining profits, higher production costs, decreased efficiency, and difficulty managing your workforce.
Q: What can I do to avoid diseconomies of scale?
A: Invest in good management, optimize your processes, embrace technology, focus on quality, and be adaptable.
Q: Is it always bad to experience diseconomies of scale?
A: Not necessarily. Sometimes it might make sense to scale back your operations if you’re experiencing diseconomies of scale. However, it’s important to understand the underlying causes of the problem so you can address them effectively.
Q: What are some examples of diseconomies of scale in real life?
A: A car manufacturer that builds too many factories, a tech company that hires too many developers without the right systems in place, and a restaurant that expands its menu without enough kitchen staff.
See more here: When Diseconomies Of Scale Occur, The Long Run? | When Diseconomies Of Scale Occur Quizlet
Economies & Diseconomies of scale Flashcards | Quizlet
Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm increases output and this leads to an increase in average cost of production. Quizlet
Diseconomies of scale Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like when do they occur, what are the different reasons all caused by, 3 reasons why diseconomies of scale Quizlet
Diseconomies of Scale Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Diseconomy of Scale, Result of Diseconomies of Scale, Why do diseconomies of scale occur? and more. Quizlet
Economies and diseconomies of scale (video) | Khan Academy
Economies of scale exist when long run average total cost decreases as output increases, diseconomies of scale occur when long run average total cost Khan Academy
Diseconomies of Scale – Economics Help
Definition of Diseconomies of scale – when long-run average costs start to rise with increased output. Diagram and causes of diseconomies of scale. Economics Help.org
Diseconomies of Scale – Guide and Examples of
What are Diseconomies of Scale? Diseconomies of scale occur when an additional production unit of output increases marginal costs, which results in reduced profitability. Instead of production costs declining as Corporate Finance Institute
Diseconomy of Scale: What it is, Why it Happens – Investopedia
Diseconomies of scale occur when a business expands so much that the costs per unit increase. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function. Investopedia
Diseconomies of Scale Definition: Causes and Types
Diseconomies of scale occur when a business expands so much that the costs per unit increase. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function. Investopedia
Diseconomies of scale – Wikipedia
The concept of diseconomies of scale is the opposite of economies of scale. It occurs when economies of scale become dysfunctional for a firm. In business, diseconomies of scale Wikipedia
Diseconomies of Scale Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like When does diseconomies of scale occur?, What do diseconomies of scale include?, What is Quizlet
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Economies Of Scale In One Minute: Definition/Theory, Explanation And Examples
A Level Business Revision – Diseconomies Of Scale
Y2 6) Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale
Economies And Diseconomies Of Scale | Apⓡ Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Economies Of Scale And Long-Run Costs- Micro Topic 3.3
Link to this article: when diseconomies of scale occur quizlet.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/