Comment faire une alkylation ?
Dans une unité d’alkylation, les gaz réactants sont mis sous pression, liquéfiés et mélangés avec un catalyseur acide, soit du HF ou du H2SO4. Dans un autre procédé d’alkylation, une zéolite solide est utilisée comme catalyseur.
Comment s’appelle la réaction du benzène avec l’acide sulfurique ?
Sulfonation. Mécanisme de la sulfonation du benzène. Le benzène réagit avec l’acide sulfurique concentré ou l’oléum (SO3 dissout dans l’acide sulfurique) pour donner l’acide benzènesulfonique selon une réaction de sulfonation.
Pourquoi ajouter de l’acide sulfurique dans le milieu réactionnel ?
L’acide sulfurique est un catalyseur de la réaction d’estérification, donc tout comme l’augmentation de température, sa présence accélère la transformation chimique.
Pourquoi il faut toujours verser l’acide dans l’eau et jamais l’inverse ?
Des projections de liquide corrosif peuvent aussi survenir. Lorsqu’on doit faire un mélange eau-acide, afin de minimiser ces dangers, il est important de dissoudre l’acide dans l’eau, et non l’inverse. L’eau absorbe et disperse la chaleur produite par la réaction, ce que l’acide ne fait pas dans le cas contraire.
Quel métal ne réagit pas à l’acide sulfurique dilué ?
L’acide dilué attaque le zinc, le fer, certaines fontes et le cuivre, mais n’a pas d’action sur le plomb.
Qu’est-ce qui résiste à l’acide sulfurique ?
Les lignes d’évent des stockage doivent résister à l’acide. Pour l’acide sulfurique, le PVC est recommandé mais pour l’oléum, l’inox 316 ou l’acier revêtu PTFE est préférable.
Quel est l’acide le plus puissant au monde ?
L’acide sulfurique est l’acide le plus fort de notre liste avec une valeur pKa de -10, donc HSO4- est la base conjuguée la plus faible. Vous pouvez voir que l’ion hydroxyde est une base plus forte que l’ammoniac (NH3), car l’ammonium (NH4+, pKa = 9,2) est un acide plus fort que l’eau (pKa = 15,7).
Quel acide dissout le sable ?
L’acide phosphorique (ou acide orthophosphorique) est un composé chimique de formule H3PO4.
Quel acide fait fondre les os ?
L’acide fluorhydrique (HF) n’est pas un acide comme les autres. C’est un puissant corrosif et un agent décalcifiant redoutable (très forte affinité pour le calcium avec fixation possible dans les dents, les os et le sang).
Quelle est la différence entre de l’acide chlorhydrique et de l’acide sulfurique ?
A concentration identique, l’acide sulfurique a un pouvoir acide supérieur à celui de l’acide chlorhydrique. L’Acti pH minus liquide contient 50 % d’acide sulfurique, alors que l’acide chlorhydrique est vendu avec 33 % de matière active.
Pourquoi HCL n’attaque pas le cuivre ?
Le cuivre étant moins réactif que l’hydrogène, il ne pourra pas remplacer l’hydrogène dans l’acide chlorhydrique. Et par conséquent, aucune réaction ne se produira.
Quelle est l’acide le plus dangereux ?
L’acide fluorhydrique peut causer une brûlure chimique unique et extrêmement dangereuse pour les victimes. Sa lipophilicité permet une absorption profonde et systémique pouvant causer des convulsions, des arythmies et une nécrose liquéfiante des tissus cutanés.
Qu’est-ce qui neutralise l’acide sulfurique ?
On peut neutraliser un déversement d’acide sulfurique concentré à l’aide de bicarbonate de sodium (bicarbonate de soude) sans trop de danger, tandis que le neutraliser avec de l’hydroxyde de sodium pourrait produire beaucoup de chaleur et de vapeurs.
Est-ce que l’acide sulfurique attaque le PVC ?
Au niveau de vos canalisations, ce produit chimique peut endommager les éléments en PVC, en fibrociment et en fonte, et engendrer d’importantes dépenses en réparation. À l’instar de la soude caustique, l’acide sulfurique est particulièrement dangereux en raison de son côté hautement corrosif.
Est-ce que l’acide sulfurique est dangereux pour la peau ?
Peut causer la mort. Effets d’une exposition de longue durée (chronique) : À faibles concentrations : Peut causer une peau sèche, rougeâtre et gercée (dermatite) à la suite d’un contact cutané. À fortes concentrations : Peut user l’émail des dents en cas d’inhalation. Peut affecter le système respiratoire.
Comment faire l’estérification ?
Pour produire l’ester, il faut prélever les réactifs puis les mettre en contact afin qu’ils interagissent. L’éthanoate de 3-méthylbutyle, nommé aussi acétate d’isoamyle, est un ester à l’odeur de banane. Pour le synthétiser, on fait réagir de l’acide éthanoïque (acide carboxylique) avec du 3-méthylbutan-1-ol (alcool).
Comment faire une Hydrogenation ?
Cette opération se fait industriellement pour transformer une huile végétale liquide en une margarine solide à température ambiante. L’opération se réalise à chaud (100 à 200 °C), l’hydrogène étant introduit sous pression.
Comment préparer les alcènes ?
Pour préparer des alcènes, autrement dit former des doubles liaisons C=C, on peut soit réaliser des réactions d’élimination à partir de composés saturés, soit réaliser des réactions d’addition à partir d’alcynes (ouvrir une triple liaison).
Comment se creer une liaison peptidique ?
Deux molécules d’acides aminés combinées forment une liaison peptidique. Une fois combinés, les acides aminés ont des groupes fonctionnels libres qui peuvent créer d’autres liaisons avec d’autres molécules d’acides aminés. C’est ainsi que se forment les polypeptides.
What is Friedel Crafts acylation?
What is Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction?
What is Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
Why do Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions result in a carbocation rearrangement?
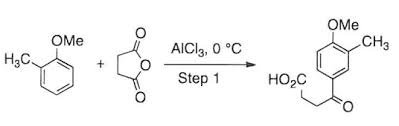
Alright, let’s talk Acylation de Friedel-Crafts, a super important reaction in organic chemistry. It’s a way to add an acyl group (think of it as a carbon double bonded to an oxygen with an alkyl group attached) to an aromatic ring. It’s super useful in making all sorts of organic compounds.
The Basics
Imagine you have a benzene ring. It’s a super stable molecule, but it can react with the right reagents. Acylation de Friedel-Crafts uses an acyl halide and a Lewis acid catalyst like aluminum chloride (AlCl3) to add that acyl group to the ring. It’s like adding a new building block to your molecule.
The Steps
1. Activation: The Lewis acid catalyst, like AlCl3, reacts with the acyl halide, like acetyl chloride (CH3COCl), forming a complex. This complex is super reactive, and it’s ready to attach to the aromatic ring.
2. Electrophilic Attack: The activated complex acts as an electrophile, meaning it’s attracted to electron-rich areas. The benzene ring is electron-rich, and the electrophile attacks the ring, forming a sigma complex.
3. Proton Loss: The sigma complex is unstable, so it loses a proton, regenerating the aromatic ring and forming the acylated product.
Let’s Get Specific
Now, let’s talk about some key aspects of this reaction:
* Mechanism: The Acylation de Friedel-Crafts reaction is a two-step process involving a carbocation intermediate. The Lewis acid acts as a catalyst by helping to generate the carbocation.
* Acylating Agents: Common acylating agents used in this reaction include acyl halides and acid anhydrides. These guys are the ones providing the acyl group.
* Lewis Acid Catalysts: The most popular Lewis acid catalyst is aluminum chloride (AlCl3). It’s super effective at activating the acyl halide for the attack on the aromatic ring.
* Aromatic Substrate: The aromatic substrate can be benzene or any substituted benzene. The substituents can affect the reaction’s outcome, determining where the acyl group attaches to the ring.
* Limitations: Remember, this reaction has its limits. It won’t work on strongly deactivated aromatic rings, and it can sometimes lead to multiple acylations if you’re not careful.
Examples of Acylation de Friedel-Crafts
Here are some examples of how this reaction is used in real-world applications:
* Ketone Synthesis:Acylation de Friedel-Crafts is a cornerstone of ketone synthesis. It’s a powerful tool for making ketones with various substituents.
* Drug Synthesis: This reaction is used in the synthesis of many pharmaceuticals, including aspirin and ibuprofen.
* Polymer Synthesis: The reaction is also important in the production of polymers like polyesters and polyamides.
Understanding the Chemistry
To really grasp Acylation de Friedel-Crafts, we need to look at the underlying chemistry.
* Acyl Group: This is the key to the reaction. It’s a carbonyl group (C=O) with an alkyl group attached. You can think of it as a building block that adds complexity to your molecule.
* Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: This is the type of reaction Acylation de Friedel-Crafts falls under. It involves an electrophile (the activated acyl group) attacking an electron-rich aromatic ring.
The Power of Friedel-Crafts
This reaction is a big deal in organic chemistry. It’s versatile and can be used to make a wide range of compounds. It’s used in industry and research, playing a crucial role in the production of useful materials and drugs.
Let’s Discuss FAQs
Now, let’s tackle some common questions about Acylation de Friedel-Crafts:
1. What are the conditions for Acylation de Friedel-Crafts?
Typically, the reaction is run in a non-polar solvent, like dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), at low temperatures to minimize side reactions. Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) is often used as the catalyst.
2. Can you use other Lewis acids besides AlCl3?
Absolutely! Other Lewis acids, like FeCl3, ZnCl2, and BF3, can also be used. The choice depends on the specific reaction and desired outcome.
3. What are the limitations of Acylation de Friedel-Crafts?
As mentioned earlier, the reaction has its limitations. It won’t work on strongly deactivated aromatic rings, and you might get multiple acylations if you’re not careful.
4. Can you use Acylation de Friedel-Crafts for other reactions?
Yes! You can modify the reaction conditions or reagents to create related reactions, like alkylation de Friedel-Crafts.
5. How do I choose the right acylating agent?
The choice of the acylating agent depends on the desired product and the reaction conditions. Acyl chlorides are generally more reactive than acid anhydrides.
6. How do I determine the position of the acyl group on the aromatic ring?
The position of the acyl group is influenced by the substituents on the aromatic ring. Electron-donating groups (like methyl groups) direct the acyl group to the ortho and para positions, while electron-withdrawing groups (like nitro groups) direct it to the meta position.
7. How do I minimize side reactions?
Low temperatures and appropriate stoichiometry can minimize side reactions. You can also use a less reactive acylating agent or change the catalyst.
8. What are the safety precautions for Acylation de Friedel-Crafts?
Acyl halides and Lewis acids are corrosive and can be dangerous if not handled carefully. Always wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, when working with these materials.
9. How do I clean up after Acylation de Friedel-Crafts?
After the reaction, you’ll need to quench the reaction mixture with water or ice. The aluminum chloride will dissolve, and the organic product will be extracted. You can then wash the organic layer with water and dry it over a drying agent like sodium sulfate.
10. Where can I learn more about Acylation de Friedel-Crafts?
You can find more information in organic chemistry textbooks and online resources like Wikipedia and Chemistry LibreTexts.
Final Thoughts
Acylation de Friedel-Crafts is a powerful tool in organic chemistry, enabling the synthesis of a vast array of compounds. It’s essential to understand the reaction’s mechanism and limitations to use it effectively and safely.
If you have any further questions, don’t hesitate to ask! We’re always here to help you learn and explore the fascinating world of organic chemistry!
See more here: Comment S’Appelle La Réaction Du Benzène Avec L’Acide Sulfurique ? | Acylation De Friedel Et Crafts
Acylation de Friedel-Crafts – YouTube
Acylation de Friedel-Crafts – YouTube. KhanAcademyFrancophone. 368K subscribers. Subscribed. 202. 22K views 8 years ago Composés aromatiques. Le YouTube
4.10: Alkylation and Acylation of Aromatic Rings – The
write an equation for a typical Friedel-Crafts acylation. write the detailed mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction. identify the product formed by the Chemistry LibreTexts
Friedel-Crafts Acylation – Organic Chemistry Portal
Friedel-Crafts Acylation. This electrophilic aromatic substitution allows the synthesis of monoacylated products from the reaction between arenes and acyl chlorides or anhydrides. The products are deactivated, and do Organic Chemistry Portal
Friedel-Crafts Acylation – Chemistry LibreTexts
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation was first discovered by French scientist Charles Friedel and his partner, American scientist James Crafts, in 1877. This reaction allowed Chemistry LibreTexts
Friedel–Crafts reaction – Wikipedia
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and Wikipedia
Acylation de Friedel-Crafts (vidéo) | Khan Academy
Khan Academy est une ONG qui a pour mission d’offrir un enseignement gratuit et de qualité, pour tout le monde, partout. … Acylation de Friedel-Crafts . Google Khan Academy
18.2 Friedel Crafts Alkylation and Acylation | Organic Chemistry
Chad gives a thorough presentation covering Friedel-Crafts Alkylation and Friedel-Crafts Acylation. He begins with the mechanism of the Friedel-Crafts Alkyl… YouTube
Friedel‐Crafts Acylation – Major Reference Works – Wiley Online
The electrophilic aromatic substitution by an acyl group derived from carboxylic acid derivatives in the presence of a Lewis acid or Brønsted acid is generally Wiley Online Library
Friedel-Crafts Acylation and Alkylation – ChemTalk
The purpose of the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is to synthesize a monoacylated aromatic ring. This reaction occurs when a carboxylic acid chloride (R-COCl) reacts with an aromatic ring in the presence of a ChemTalk
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Acylation De Friedel-Crafts
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
87/213 Mécanisme D’Alkylation De Friedel Et Crafts
89/213 Acyaltion De Friedel Et Crafts
25. Benzene Partie 4/8: Substitution Électrophile Aromatique (Acylation De Friedel Et Crafts)
Link to this article: acylation de friedel et crafts.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/