What is responsible for converting fibrinogen to fibrin?
Fibrinogen is converted by thrombin into fibrin and stabilized by factor XIII. Fibrin sticks to the tissue and the tissue is adapted by syneresis. Local application of aprotinin to the thrombin solution is necessary in order to inhibit premature lysis of the fibrin film.
How do you convert fibrinogen to fibrin?
Fibrinogen is a soluble macromolecule, but forms an insoluble clot or gel on conversion to fibrin by the action of the serine protease thrombin, which is activated by a cascade of enzymatic reactions triggered by vessel wall injury, activated blood cells, or a foreign surface (Fig.
Which enzyme converts fibrinogen to fibrin?
Enzyme thrombin catalyzes the conversion of soluble plasma proteins fibrinogen into insoluble fibrous protein fibrin. Fibrin makes a mesh-like structure around the platelet plug made initially and the blood cells are trapped in this mesh to form a clot.
Which of the following catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin?
[6] Factor IIa, or as commonly known, thrombin, catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin.
What is the conversion of fibrin to fibrinogen catalysed by?
So, the correct answer is ‘Thrombin‘
What activates fibrinogen to fibrin?
Factor IIa (thrombin) goes on to activate fibrinogen into fibrin. Thrombin also goes on to activate other factors in the intrinsic pathway (factor XI) as well as cofactors V and VIII and factor XIII. Fibrin subunits come together to form fibrin strands, and factor XIII acts on fibrin strands to form a fibrin mesh.
Which factor converts fibrinogen into fibrin?
Thrombin is an endogenous protein involved in the coagulation cascade, where it has a key role in the formation of fibrin clots by converting fibrinogen to fibrin.
What substance is needed to convert fibrinogen to fibrin?
Thrombokinase in the presence of calcium converts prothrombin into thrombin, which in turn converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
Which enzyme catalyzes the formation of fibrin?
Thrombin, in turn, catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen (factor I)—a soluble plasma protein—into long, sticky threads of insoluble fibrin (factor Ia). The fibrin threads form a mesh that traps platelets, blood cells, and plasma.
What converts fibrinogen to fibrin threads?
When tissue damage results in bleeding, fibrinogen is converted at the wound into fibrin by the action of thrombin, a clotting enzyme.
Which enzyme blank converts fibrinogen into fibrin?
Answer and Explanation: Thrombin is the enzyme that converts fibrinogen in the blood to fibrin, forming a clot which envelopes bacteria.
Which enzyme induces lysis of fibrinogen to fibrin?
So, the correct answer is ‘Plasmin‘.
What helps in converting fibrinogen into fibrin?
Thrombin acts as an enzyme and convert fibrinogen into fibrin threads which form clot at the wound site.
What converts fibrinogen to fibrin monomer?
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalyzed by the serine protease thrombin, which is generated by the blood coagulation cascade from the activation of prothrombin.
What catalyzes fibrinogen?
Thrombin catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by cleaving, in sequence, the N-termini of the α chain, releasing fibrinopeptide A (FpA), and the β chain, releasing fibrinopeptide B (FpB) (Lord, 2007; Wolberg, 2007).
What is the enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin called?
Thrombin is a serine peptidase (EC 3.4. 21.5.) that is found in blood and converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalysing many other coagulation-related reactions.
Is fibrinogen converted into fibrin by thrombokinase?
Thromboplastin also called thrombokinase is a combination of phospholipids and tissue factors in plasma that catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Fibrinogen is a clotting factor present in the plasma. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin with the help of thrombin.
What catalyzes the polymerization of fibrinogen into strands of fibrin?
Thrombin (factor IIa) is the central player in clot formation (Fig. 3-1). Thrombin, a serine protease, cleaves fibrinogen to generate fibrin, which forms the scaffolding for the growing thrombus.
Which factor coagulation transforms fibrinogen to fibrin?
Thrombin acts on fibrinogen molecules to convert them to fibrin monomers. These monomers form an instantaneous clot by associating via noncovalent bonds.
What converts fibrinogen to fibrin quizlet?
Fibrinogen is converted to Fibrin by the enzyme Thrombin. The mesh for clot formation is formed by individual fibrin threads.
What bacteria converts fibrinogen to fibrin?
Staphylococcal enzymes Coagulase is the enzyme which catalyses the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. It is most closely associated with pathogenicity, having previously been used in the microbiology laboratory to separate pathogens from non-pathogens.
What catalyzes the transformation of fibrinogen to fibrin?
The thrombin-catalyzed conversion of fibrinogen (F) to fibrin consists of three reversible steps, with thrombin (T) being involved in only the first step which is a limited proteolysis to release fibrinopeptides (FpA and FpB) from fibrinogen to produce fibrin monomer.
What is the pathway of fibrinogen to fibrin?
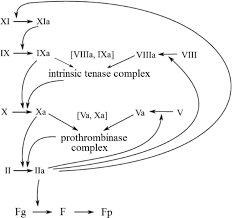
The common pathway begins when factor Xa, Va, and calcium bind together, forming a prothrombinase complex. The prothrombinase complex then activates prothrombin (factor II) into thrombin (factor IIa). Next, thrombin cleaves fibrinogen (factor I) into fibrin (factor Ia).
What converts fibrinogen to soluble fibrin?
Assertion :Fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive fibrinogens in the plasma by the enzyme thrombin.
What involves the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin?
The final steps in the coagulation cascade involve the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin monomers which polymerizes and forms fibrin polymer mesh and result in a cross-linked fibrin clot.
Which of the following substances directly converts fibrinogen into fibrin?
Thrombin is a serine protease that plays a crucial role in blood clot formation by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating other zymogens involved in clotting.
Which factor converts fibrinogen into fibrin?
Thrombin is an endogenous protein involved in the coagulation cascade, where it has a key role in the formation of fibrin clots by converting fibrinogen to fibrin.
What converts fibrinogen to fibrin threads?
When tissue damage results in bleeding, fibrinogen is converted at the wound into fibrin by the action of thrombin, a clotting enzyme.
What substance is needed to convert fibrinogen to fibrin?
Thrombokinase in the presence of calcium converts prothrombin into thrombin, which in turn converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
Which blood cell causes fibrinogen to become fibrin?
When the lining of a blood vessel is broken, platelets are attracted, forming a platelet plug. These platelets have thrombin receptors on their surfaces that bind serum thrombin molecules, which in turn convert soluble fibrinogen in the serum into fibrin at the wound site.
How is fibrin converted into fibrin?
What is the role of fibrinogen in hemostasis?
How is fibrinogen converted to thrombin?
What is a model of fibrin formation based on?
Imagine you get a paper cut, or a scrape on your knee. The first line of defense is blood clotting. It’s how our bodies stop bleeding and seal up those wounds. And at the center of this whole process is the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
Fibrinogen is a soluble protein that floats around in our blood. It’s kind of like the dormant superhero waiting for the call to action.
Fibrin on the other hand, is an insoluble protein. It’s the active hero that forms those important blood clots to stop the bleeding.
Now, how does this conversion happen?
It’s all thanks to thrombin, a powerful enzyme. It’s the catalyst that makes this transformation possible.
Think of it like this:
* Fibrinogen is like a raw ingredient – it’s got the potential, but it’s not ready to do its job.
* Thrombin is the chef – it knows exactly how to transform the fibrinogen into a powerful, clot-forming fibrin.
So, what happens when you get a cut?
1. Damage to blood vessels triggers a cascade of events. Think of it like a chain reaction.
2. This leads to the activation of thrombin.
3. Thrombin then cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin monomers. These monomers then assemble into long, fibrous strands.
4. These strands form a mesh-like network that traps blood cells and platelets, creating a stable clot.
This whole process is crucial for stopping bleeding, preventing infections, and helping our bodies heal.
Here’s a breakdown of the key players:
Fibrinogen: The precursor to fibrin. It’s the inactive form that’s waiting to be transformed.
Thrombin: The enzyme responsible for converting fibrinogen into fibrin. It’s the catalyst that sets the whole process in motion.
Fibrin: The insoluble protein that forms the mesh-like network of the blood clot. It’s the hero that stops the bleeding and seals the wound.
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into thrombin’s role.
Thrombin is a serine protease, which means it’s an enzyme that cuts proteins.
* It has a specific site on fibrinogen where it cleaves.
This cleavage releases fibrinopeptides, small protein fragments.
The release of these fragments exposes binding sites on the fibrin molecule.
These binding sites allow fibrin molecules to assemble into those long, fibrous strands, forming the clot.
But there’s more to it than just thrombin.
Other factors play a role in fibrinogen-to-fibrin conversion. These include:
Calcium ions: They’re essential for thrombin activity.
Factors V and VIII: These factors help activate prothrombin, the precursor of thrombin.
Platelets: They release factors that activate the clotting cascade.
So, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is a complex process with many players. But it’s a vital one for our health. It allows us to stop bleeding and heal from wounds.
Now, let’s talk about some common questions people have about fibrinogen and fibrin.
FAQs
1. What happens if fibrinogen levels are low?
Low fibrinogen levels can lead to increased bleeding and difficulty forming blood clots. This can happen due to:
Liver disease: The liver is where fibrinogen is made.
Certain medications: Some medications can affect fibrinogen production.
Genetic disorders: Some genetic conditions can lead to low fibrinogen levels.
2. What happens if fibrinogen levels are high?
High fibrinogen levels can increase the risk of blood clots. This can happen due to:
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can lead to high fibrinogen levels.
Pregnancy: Fibrinogen levels naturally increase during pregnancy.
Cancer: Some types of cancer can lead to high fibrinogen levels.
3. Can I control my fibrinogen levels?
You can’t directly control your fibrinogen levels. However, you can manage the factors that contribute to high or low levels. These include:
Managing chronic diseases: Control your diabetes, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
Eating a healthy diet: Limit processed foods and saturated fats.
Staying active: Regular exercise is good for your overall health, including your blood vessels.
Quitting smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots.
4. What are the treatments for fibrinogen deficiencies?
Treatments for fibrinogen deficiencies depend on the severity of the condition.
Mild deficiencies may not require treatment.
Moderate to severe deficiencies can be treated with fibrinogen concentrates or cryoprecipitate.
5. What are the treatments for high fibrinogen levels?
The best treatment for high fibrinogen levels depends on the underlying cause.
Treatment for the underlying cause: This may include addressing inflammation, managing cancer, or adjusting medications.
Blood thinners: In some cases, blood thinners may be prescribed to prevent blood clots.
6. How can I learn more about fibrinogen and fibrin?
Talk to your doctor: Your doctor can provide you with personalized information and advice.
Consult reliable websites: Check out websites from reputable medical organizations, like the Mayo Clinic or the National Institutes of Health.
Understanding fibrinogen and fibrin is essential for understanding how our bodies heal and stop bleeding. These proteins are key players in the complex process of blood clotting, and it’s important to be aware of their role and potential problems related to their levels. Remember, if you have any concerns about fibrinogen or fibrin levels, talk to your doctor.
See more here: How Do You Convert Fibrinogen To Fibrin? | Conversion Of Fibrinogen To Fibrin Is Catalysed By
The Conversion of Fibrinogen to Fibrin: Recombinant Fibrinogen
In the fluid phase, fibrinogen is converted to fibrin in a reaction catalyzed by thrombin, which releases fibrinopeptides A (FpA) and B (FpB) from the amino-termini of the Aα and Bβ chains, respectively, and produces fibrin monomers. American Society of Hematology
Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties – PMC – National
On cleavage of fibrinopeptides by thrombin, fibrinogen is converted to fibrin monomers, which interact via knobs exposed by fibrinopeptide removal in the central region, with National Center for Biotechnology Information
Fibrinogen replacement therapy: a critical review of the literature
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalysed by thrombin and plays a key role in clot formation and stabilisation. In addition, fibrinogen induces platelet National Center for Biotechnology Information
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin: A brief history of some key …
Quite apart from its physiological importance, the transformation of fibrinogen to fibrin on its own has held a legion of researchers in thrall. The rapid conversion of ScienceDirect
Fibrinogen and fibrin: An illustrated review – PMC
Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin, which stabilizes blood clots and promotes hemostasis. Fibrin structure and mechanical properties are modified by genetic and National Center for Biotechnology Information
Fibrinogen and fibrin: An illustrated review – Pieters
Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin, which stabilizes blood clots and promotes hemostasis. Fibrin structure and mechanical properties are modified by genetic and environmental factors. Fibrin(ogen) also Wiley Online Library
Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions
Schematic diagram of fibrinogen structure, its conversion to fibrin, and the thrombin-mediated conversion of native factor XIII to XIIIa. Binding sites for proteins, enzymes, receptors, and other molecules that Wiley Online Library
The Fibrinogen-Fibrin Conversion – ScienceDirect
The chapter explores four of the processes by which the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin takes place. These are (1) activation by citrate, (2) activation by calcium ions, ScienceDirect
Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalysed by (a) thrombin (b …
The conversion can be summarized in simple steps for clarity: Fibrinogen, present in the blood, encounters activated thrombin. Thrombin cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin vaia.com
Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions – Journal
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of fibrinogen structure, its conversion to fibrin, and the thrombin‐mediated conversion of native factor XIII to XIIIa. Binding sites for proteins, enzymes, receptors, and other molecules that jthjournal.org
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Conversion Of Fibrinogen To Fibrin Is Catalysed By (A) Thrombin (B) Prothrombin (C) Thrombopla…
Conversion Of Fibrinogen To Fibrin Is Catalysed By
Fibrinogen | Factor I | Fibrin |
Fibrin Degradation Animation Video
Platelet Activation And Factors For Clot Formation
Link to this article: conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalysed by.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/