What is the difference between Amphiprotic and amphoteric IB?
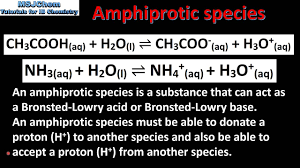
Amphiprotic species: is a compound which is able to gain a hydrogen ion to form a conjugate acid or lose a hydrogen ion to form a conjugate base. Thus these species act as both a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base. Amphoteric species: Can act as either a base or an acid. All amphiprotic species are also amphoteric.
Is water amphoteric or amphiprotic?
Expert-Verified Answer. Water is considered amphoteric and amphiprotic due to its ability to act as both an acid and a base in different chemical reactions. Amphoteric substances can exhibit both acidic and basic properties depending on the context of the reaction.
What is the difference between amphoteric and Polyprotic?
Amphoteric means it can act as either an acid or a base and is just generally a more broad definition. It is a subtle difference but I think it will be more important in later chemistry courses. Polyprotic just means it can donate multiple H+ protons.
What is the difference between amphoteric and buffer?
There is a distinct difference between amphoteric substances and buffers, which is easily overlooked, when starting to work with acid/base chemistry, amphoteric substances are one molecule or one ion having both functions, whereas buffers are mixtures of acid and base, i.e. two different molecules/ions.
Are amphiprotic and amphoteric the same?
Answer and Explanation: When an amphiprotic substance donates or accepts protons, it also acts as an acid or base (Bronsted-Lowry definition), hence, it is also amphoteric. All amphiprotic substances are amphoteric but not all amphoteric substances are amphiprotic.
Is H2PO4 amphiprotic?
Answer and Explanation: The given substance H 2 P O 4 − is an amphiprotic substance. Dihydrogen phosphate is able to donate its ionizable proton and accept a proton from a water molecule.
Is HS − amphiprotic?
The hydrosulfide ion is known to be an amphiprotic compound.
Is HPO4 2 amphiprotic?
a) The hydrogen phosphate ion, H P O 4 2 − (aq), is amphiprotic and can act as an acid or base.
Is amphoteric same as Amphipathic?
A molecule with both a polar and non-polar parts is known as amphipathic. The word amphoteric means a molecule that can act as either an acid or a base.
What is another name for Amphiprotic?
Definitions of amphiprotic. adjective. having characteristics of both an acid and a base and capable of reacting as either. synonyms: amphoteric.
Is HCO3 amphiprotic?
Like water, the hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3-) is amphiprotic.
What ion substance is amphoteric and Amphiprotic?
An Amphoteric substance is a substance that can act both as an acid and as a base. Water, amino acids, hydrogen carbonate ion (or bicarbonate ion) HCO3−, dihydrogen phosphate ion H2PO4–, and hydrogen sulfate ion (or bisulfate ion) HSO4– are common examples of amphiprotic species.
Why are they called amphoteric?
Amphoteric mean the compound can serve as both an acid or as a base. An amino acid can do this because it has both an amino group and a carboxylic acid group.
How to determine if a solution is amphoteric?
If the substance can act like both an acid and a base, i.e., both give and accept protons, then it’s amphoteric.
What is amphoteric with example?
Amphoteric meaning, in the simplest term, can be stated as any compound that can be mixed with other compounds both as a base and an acid. For example, water is amphoteric. It can be transformed into a compound that can be used as an alkali or an acid. Most amphoteric compounds are metal oxides or hydroxides.
Is Al2O3 amphiprotic?
It is amphoteric as it can react with both acids and bases acting as an acid with a base and a base with an acid neutralising the other and producing the salt. The formula of Aluminium oxide is Al2O3.
Is H2SO4 amphiprotic?
Another example of an amphiprotic compound is hydrogen sulfate, HSO4-. It can receive a proton to become sulfuric acid, H2SO4, or it can lose a proton to become sulfate, SO42–. Often, both terms will be used interchangeably because all amphiprotic compunds are also amphoteric.
Why isn’t H3PO4 amphiprotic?
This is phosphoric acid. If you are, it isn’t amphoteric because it won’t readily accept a proton to act as a base. It is only acidic. It will donate a proton to form H2PO−4.
What is an example of amphoteric but not Amphiprotic?
So aluminium oxide can act as both an acid and a base – and so is amphoteric. But it isn’t amphiprotic because both of the acid reaction and the base reaction don’t involve hydrogen ions.”
Is H3PO4 2 amphiprotic?
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is a weak acid that can donate protons, making it amphiprotic. It readily donates three protons in sequential steps, resulting in the formation of dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4-), hydrogen phosphate (HPO42-), and finally, phosphate ions (PO43-). Therefore, H3PO4 is amphiprotic.
Is H3O+ amphiprotic?
H3O+ is the protonated and acidic form of H2O. It can not accept another proton to become H4O+2, and so it can also not act as a base (bronsted). Therefore, no, it is not amphoteric.
Is HNO2 amphiprotic?
Nitrous acid, H N O 2 , is an acid so it is less likely to accept a proton. Hence, it is NOT AMPHIPROTIC.
Why is NH4+ not amphoteric?
An amphiprotic substance is one which can both gain and lose a proton. NH4+ can lose a proton to form NH3, but NH4+ cannot gain a proton to form NH5^2+. Consequently, NH4+ is not amphiprotic.
Is HCO3 amphiprotic or amphoteric?
Amphiprotic Species For example, the hydrogen carbonate ion HCO3– is amphiprotic.
Is HSO3 amphiprotic?
The hydrogen sulfite ion (HSO3−) is amphiprotic.
Is HNO3 Amphiprotic?
HNO3 is a strong acid and can only donate H+ ions hence, it is not amphoteric in nature. Which one of the following is not an amphoteric substance?
What is the difference between amphoteric and basic oxides?
An acidic oxide is an oxide that when combined with water gives off an acid. A basic oxide is an oxide that when combined with water gives off a base. When a substance reacts chemically, both as a base or acid is termed as amphoteric oxide. Neutral Oxide is one that neither has an acidic characteristic nor a basic one.
What ion substance is amphoteric and Amphiprotic?
An Amphoteric substance is a substance that can act both as an acid and as a base. Water, amino acids, hydrogen carbonate ion (or bicarbonate ion) HCO3−, dihydrogen phosphate ion H2PO4–, and hydrogen sulfate ion (or bisulfate ion) HSO4– are common examples of amphiprotic species.
What is the difference between amphoteric and metalloids?
To be amphoteric you must be able to act as an acid or base. Metalloids, because they’re in between metals and non metals, are more likely to be able to play the role of either electron acceptor/donor (Lewis definition) and proton donor/acceptor (Bronsted definition).
What does amphoteric mean Igcse?
Amphoteric oxides Amphoteric oxides are a curious group of oxides that can behave as both acidic and basic, depending on whether the other reactant is an acid or a base.
What is the difference between amphiprotic and amphoteric?
How do amphiprotic and amphoteric substances interact?
What is an example of an amphoteric compound?
What does amphoterism mean?
Let me tell you, it’s a common confusion! Even though they’re closely related, there’s a key difference between them, and understanding that difference is crucial when studying chemistry.
Think of it this way: Imagine you have a substance that can act as both a donor and an acceptor. Sounds pretty versatile, right? That’s basically what both amphiprotic and amphoteric substances are all about. But, let’s break down the key distinctions.
What’s Amphiprotic?
Imagine a substance that can donate protons (*H+*). That’s your basic acid, right? But now imagine that same substance can also accept a proton. This is where the amphiprotic concept comes in.
Amphiprotic substances are species that can donate protons (*H+*) in a reaction (acting as an acid) and also accept protons (*H+*) in a different reaction (acting as a base). They have this special ability to act as both an acid and a base by using proton transfer.
Let’s take a look at some examples:
Water (H2O): In the presence of a strong acid, water acts as a base by accepting a proton. In the presence of a strong base, water acts as an acid by donating a proton.
Hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3-): This ion can donate a proton to form carbonate ion (CO32-), acting as an acid. Alternatively, it can accept a proton to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), acting as a base.
Key Takeaways for Amphiprotic Substances:
Proton transfer is the main mechanism.
* They can act as acids by donating protons and as bases by accepting protons.
Water is a classic example, along with bicarbonate ions.
What’s Amphoteric?
Now, let’s talk about amphoteric substances. This category is slightly broader, but it also includes amphiprotic substances. So, all amphiprotic substances are amphoteric, but not all amphoteric substances are amphiprotic.
Let me explain.
Amphoteric substances are compounds that can react with both acids and bases. However, their reactions might not always involve proton transfer.
Here’s how it works:
Reaction with an acid: An amphoteric substance can accept a proton from an acid, acting as a base.
Reaction with a base: An amphoteric substance can donate a proton or a positively charged species like a metal ion to a base, acting as an acid.
Metal hydroxides, like aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3), are good examples. They can react with acids to form salts and water:
“`
Al(OH)3(s) + 3HCl(aq) → AlCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
“`
They can also react with bases to form complex ions:
“`
Al(OH)3(s) + OH-(aq) → [Al(OH)4]-(aq)
“`
Key Takeaways for Amphoteric Substances:
* They can react with both acids and bases.
* Reactions don’t always involve proton transfer.
* They can act as acids by donating protons or other positively charged species and as bases by accepting protons.
The Big Difference:
Now, let’s get to the core of the difference:
Amphiprotic substances use proton transfer to act as both an acid and a base. Think of water. It donates a proton when it acts as an acid and accepts a proton when it acts as a base.
Amphoteric substances can react with both acids and bases, but their reactions don’t always involve proton transfer. Think of aluminum hydroxide. It can react with acids and bases without always using proton transfer.
Think of it this way: Amphiprotic substances are like the chameleon of the chemical world. They change their behavior (acidic or basic) based on the environment. Amphoteric substances are broader and include the chameleons (the amphiprotic substances) and other substances that can act as both an acid and a base through different mechanisms.
A Table to Visualize:
Here’s a table to further illustrate the difference:
| Feature | Amphiprotic | Amphoteric |
|—|—|—|
| Definition | Substances that donate protons (*H+*) as acids and accept protons (*H+*) as bases. | Substances that react with both acids and bases. |
| Mechanism | Proton transfer | May or may not involve proton transfer. |
| Examples | Water (H2O), bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) | Water (H2O), aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3), zinc oxide (ZnO) |
FAQs:
1. Are all amphiprotic substances amphoteric?
Yes, all amphiprotic substances are amphoteric, but not all amphoteric substances are amphiprotic. This is because amphoterism is a broader term.
2. How can I tell if a substance is amphiprotic?
Look for substances that can donate and accept protons (*H+*) through proton transfer. Think of water.
3. How can I tell if a substance is amphoteric?
Look for substances that react with both acids and bases. Remember that these reactions don’t always involve proton transfer. Think of aluminum hydroxide.
4. Is there a simple way to remember the difference?
Think of it this way: Amphiprotic substances specifically use proton transfer. Amphoteric substances are more general and encompass those that use proton transfer and other mechanisms.
Remember, amphiprotic and amphoteric substances might seem confusing, but with a little practice and understanding, you’ll be able to confidently differentiate between them.
See more here: Is Water Amphoteric Or Amphiprotic? | Difference Between Amphiprotic And Amphoteric
Amphiprotic vs. Amphoteric — Comparison & Examples – Expii
Amphiprotic vs. Amphoteric — Comparison & Examples. Amphoteric species can act as both an acid and base. Amphiprotic species can both donate and accept protons, Expii
Amphiprotic vs. Amphoteric: What’s the Difference?
Amphiprotic substances can donate or accept protons (H⁺), while amphoteric substances can act as acids or bases but not strictly through proton transfer. Difference Wiki
Amphiprotic vs Amphoteric – What’s the difference? | WikiDiff
As adjectives the difference between amphiprotic and amphoteric is that amphiprotic is (chemistry) being able to both donate and accept a proton, and thus being able to react WikiDiff
10.6: Types of Acids and Bases – Chemistry LibreTexts
Amphiprotic vs. amphoteric: what’s the difference? An amphoteric substance is one that can act as either an acid or a base. An amphiprotic substance Chemistry LibreTexts
11.12: Amphiprotic Species – Chemistry LibreTexts
Molecules or ions which can either donate or accept a proton, depending on their circumstances, are called amphiprotic species. The most important amphiprotic Chemistry LibreTexts
Amphiprotic Species | SL IB Chemistry Revision Notes 2025
What is the difference between amphiprotic and amphoteric? A compound that is amphoteric means it has both basic and acidic character. When the compound reacts savemyexams.com
7.8A: Amphoteric Behavior – Chemistry LibreTexts
Many metals (such as copper, zinc, tin, lead, aluminium, and beryllium) form amphoteric oxides or hydroxides. Amphoterism depends on the oxidation state of the oxide. For example, zinc oxide Chemistry LibreTexts
Amphoteric Definition and Examples – ThoughtCo
Amphiprotic molecules are a type of amphoteric species that either donates or accepts a proton (H +), depending on the conditions. Not all amphoteric ThoughtCo
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
8.1 What Is The Difference Between Amphiprotic And Amphoteric? [Sl Ib Chemistry]
Amphiprotic Vs Amphoteric (Ib Chemistry)
Understanding Amphoteric Species
Amphoteric Species
8.1 Amphiprotic Species (Sl)
Link to this article: difference between amphiprotic and amphoteric.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/