What is a dry cell for class 6?
Definition of Dry Cell It is a type of electric battery and consists of electrochemical cells. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy with the help of which our electronic devices work.
What is the simple structure of dry cell?
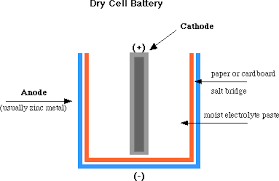
It consists of a zinc jar on one side of the cell with a narrow brass cap labelled positive (+) and a metal base on the other side of the cell labelled negative (-). A carbon rod is inserted in the cell’s middle, surrounded by a muslin bag containing a mixture of manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]) and charcoal (C).
What is a dry cell in a circuit diagram?
A dry cell is a device that generates electricity based on chemical reactions. When the two electrodes of the cell are connected via a closed path, then the cell forces the electrons to flow from one end to the other. The flow of electrons causes the current to flow in the closed circuit.
How does a dry cell work?
The dry cells convert the stored chemical energy into electrical energy. They undergo reduction-oxidation (Redox) reactions at the cathode and anode. Some dry cells can be recharged while others can be used only once. The secondary fuel cells are pollution-free and are extremely efficient in generating electricity.
What is a dry cell for kids?
Dry cells contain no free liquids; instead, the liquid is soaked up in an absorbent material or is in a paste or gel. Several cells are often used together. Connecting the cells in series—with the positive electrode of one cell to the negative electrode of the next—increases the voltage.
What is the difference between simple cell and dry cell Class 6?
Answer: Simple cell has liquid chemicals and it is difficult to carry from one place to another. Dry cell has no solution. So, it is easier to carry it from one place to another and there is no risk of spilling acid from the dry cell.
What is the shape of a dry cell?
A dry-cell battery, which is commonly used, is composed of a zinc-carbon battery that is either cuboidal or cylindrical in shape. During the electrochemical reaction, zinc is used to form the anode, and a carbon rod is used to form the cathode, which is surrounded by a mixture of carbon and manganese dioxide (MnO2).
Is a dry cell AC or DC?
Dry cells produces direct current . Was this answer helpful?
What is electric cell class 6?
Definition: An electric cell is a device, which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It has two terminals, which are made up of metal: one terminal is positive ( ), while the other one is negative ( ). When the two terminals are connected to an electrical device, electric current flows through it.
Why is it called dry cell?
The ‘dry cell’ was given this name because we use powdered manganese dioxide (MnO2) and graphite (C) with the paste of zinc chloride (ZnCl2) in it instead of liquid electrolytes.
What is dry cell class 6 short answer?
Dry cell: A dry cell is an electrochemical cell consisting of low moisture immobilized electrolytes in the form of a paste, which restricts it from flowing. Due to this, it is easily transportable. Advantages of a dry cell: They are easy to use in a simple electronic device.
What are three main components of a dry cell?
A standard dry cell comprises a zinc anode, usually in the form of a cylindrical pot, with a carbon cathode in the form of a central rod. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride in the form of a paste next to the zinc anode.
Why does a dry cell become dead?
A dry cell has an electrolyte and a couple of cathodes. A dry cell consistently has some inside obstruction. Due to this inner obstruction, there is in every case some voltage drop related with the cell regardless of whether the cell isn’t being used, and ultimately become dead after quite a while.
Why is dry cell useful to us?
A dry cell is a voltage-making cell in which the electrolyte is in the form of a moist paste. Because of this, the electrolyte doesn’t leak out, and the device can be taken anywhere. This is used in flashlights, small radios, and other things. Dry cells are things like zinc-carbon batteries and alkaline batteries.
What is the aim of dry cell?
Understanding dry cells Dry cells are electrochemical cells that contain low moisture immobilised electrolytes in the form of a paste, which prevents them from flowing freely. Because of this, it is quite portable. Electric batteries, such as dry cells, are used in household and portable electronic gadgets.
Is a dry cell easy to use?
Dry cells have high energy density or power stored to weight ratio. So they are of compact size which makes them easy to carry around which makes them one of the most common types of batteries found everywhere. Primary cells are those which cannot be recharged.
Why are dry cells better than wet cells?
Operation in any position: Unlike wet-cell batteries, dry-cell batteries can be operated in any position, useful for a wide range of applications. Efficient Power Creation: Dry-cell batteries also typically have great energy densities, packing a large amount of power into a small, efficient design.
How many types of dry cell batteries are there?
Types of dry-cell batteries are zinc-carbon batteries, alkaline-cell batteries, and mercury batteries. Before zinc-carbon batteries were used, mercury batteries were the main resource. It was not until mercury was known to become harmful that zinc-carbon batteries replaced it.
Who invented dry cell class 6?
Answer:- In 1880’s, a German scientist named Carl Gassner invented the first dry cell. Definition: A dry cell is a voltage generating cell in which the electrolyte is in the form of a moist paste. Because of this there is no spilling of electrolyte and hence becomes portable.
What is the summary of dry cell?
A dry-cell battery is a device made of one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. It contains an electrolyte that is contained within a paste or other moist medium. A Standard dry cell battery includes a zinc anode and a carbon cathode within a central rod.
Why is charcoal used in dry cells?
The powdered carbon will reduce the internal resistance of the cell and hence the metal rod on the carbon rod also acts as a positive terminal. According to the nature of the dry cell, it can be divided into two types, primary cell and the secondary cell.
Can dry cells be charged?
The chemicals in the dry cells get used over time and the reaction is irreversible. Therefore, dry cells are non-rechargeable batteries.
What does a dry cell convert into?
A dry cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Why is cell not really dry?
Dry cells are not dry because they contain electrolytes in the form of paste or gel with enough moisture. The moisture present is enough for the flow of current in the cell. This also prevents the spilling of electrolytes making them portable and compact.
What is the definition of a cell for Class 6?
“A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.” Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life.
What is wet cell class 6?
A wet-cell battery is the original type of rechargeable battery. … The battery contains a liquid electrolyte such as sulfuric acid, a dangerous corrosive liquid. A dry-cell battery does not contain liquid.
What is electric cell class 6?
Definition: An electric cell is a device, which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It has two terminals, which are made up of metal: one terminal is positive ( ), while the other one is negative ( ). When the two terminals are connected to an electrical device, electric current flows through it.
What are the advantages of dry cell Class 6 answer?
Ans. With just enough moisture to enable current passage, a dry cell has the electrolyte immobilised in a paste form. Unlike wet cells, it is possible to use a dry cell in any position without fear of spillage. It is one of the advantages of a dry cell over wet cells.
How do you explain a dry cell with diagram?
What is the structure of a zinc-carbon dry cell?
What is a dry cell in chemistry?
What are the terminals of a dry cell?
What is a Dry Cell?
Let’s get started! Imagine a tiny power plant tucked inside a metal can. That’s basically what a dry cell is. It’s like a mini battery that stores chemical energy and transforms it into electrical energy.
Think about it, electricity powers a wide range of devices we use every day. Dry cells, with their stored chemical energy, become our go-to power source. But how does this magic happen?
The Secret Behind the Magic:
The magic lies in the inner workings of a dry cell. Now, “dry cell” is a bit of a misnomer, you know? It’s not actually completely dry. There’s a moist paste inside that plays a crucial role in the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy.
The Dry Cell Diagram: A Peek Inside
Ready to explore a typical dry cell diagram? Here’s what you’ll find:
1. The Outer Case: The outermost part of the dry cell is the metal can, usually made of zinc. It serves as the negative terminal of the cell.
2. The Carbon Rod: Right in the middle of the can, you’ll spot a carbon rod, which acts as the positive terminal.
3. The Electrolyte Paste: Surrounding the carbon rod, there’s a moist paste called the electrolyte. This paste contains a mix of chemicals like ammonium chloride and manganese dioxide, which are key for the chemical reactions that generate electricity.
4. The Separator: There’s also a separator between the carbon rod and the zinc can. This separator keeps the chemicals in the electrolyte paste from directly reacting with the zinc.
The Science Behind the Dry Cell:
Now, let’s dive into the science! When you connect a dry cell to a device, here’s what happens:
* Chemical Reaction: A chemical reaction starts inside the dry cell. The chemicals in the electrolyte paste react with the zinc can, releasing electrons.
* Electron Flow: The electrons released travel from the negative terminal (the zinc can) towards the positive terminal (the carbon rod).
* Electrical Current: This flow of electrons constitutes the electrical current that powers your device.
Types of Dry Cells:
There are different types of dry cells. Some common ones are:
* Carbon-Zinc Cell: The one we’ve been talking about, with a zinc can, carbon rod, and electrolyte paste.
* Alkaline Cell: These cells use alkaline materials like potassium hydroxide in the electrolyte. They last longer than carbon-zinc cells.
* Lithium Cell: These are the champions when it comes to long shelf life and high energy density. You’ll often find them in watches, calculators, and other devices that need power for a long time.
Dry Cells: Powering Our Lives
Dry cells are essential to our daily lives. They power everything from flashlights to toys, clocks, radios, and even some medical devices.
FAQs:
Q: What is the difference between a dry cell and a battery?
A: A dry cell is basically a single unit that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. A battery is a collection of multiple dry cells connected together to provide a higher voltage or current.
Q: Why is it called a dry cell?
A: The name is a bit misleading. While it’s not completely dry, the electrolyte is a moist paste, not a liquid like in a wet cell battery.
Q: What are some precautions when using dry cells?
A: * Never mix different types of dry cells in the same device. * Dispose of them properly. * Avoid getting them wet. * Keep them away from children.
Q: Can you reuse a dry cell?
A: Unlike rechargeable batteries, dry cells are not designed to be reused. Once the chemical reaction is complete, they are considered spent.
See more here: What Is The Simple Structure Of Dry Cell? | Dry Cell Diagram For Class 6
Dry-cell – Definition, Working Principle and Types of
Dry cells are electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. Learn the definition, different types of dry cells with electrochemical reactions and examples. BYJU’S
Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 12
The Dry Cell: A dry cell is a very convenient source of electric current. The dry cell, as its name suggests, contains dry or semi-solid ingredients. Let us take a look Learn CBSE
Draw neat and labelled diagram of dry cell. – Toppr
Solution. Verified by Toppr. In the above diagram there is a dry cell with description of its parts. Was this answer helpful? 71. Similar Questions. Q 1. Draw neat and labelled Toppr
Explain the dry cell with diagram? – Toppr
Dry Cell: It is a primary cell based on Leclanche cell invented by G. Leclanche in 1868. In a primary cell, the electrode reactions cannot be reversed by an external source of electrical energy. In this cell, the cell Toppr
Dry Cell (Construction & Working) | Electricity | Class-6 … – YouTube
This topic is from NCERT BOOK of calss 6 YouTube
What is a Dry Cell : Structure & Its Working – ElProCus
Structure of Cell. The structure of the zinc-carbon dry cell is shown in the figure. It consists of zinc as the anode terminal and graphite rod as cathode terminal. But in older versions, it may be observed that in dry cell the ElProCus
Electric Cell – All you need to know!! | Class 6 Electricity and …
Enjoy learning with LearnFatafat!! 📱 Download the LearnFatafat Android App Now – https://bit.ly/3dq1DCJ🙂 Join this channel to get access to perks ⭐⭐:https:… YouTube
Electricity and Circuits Chapter 12 Class 6 Science Part 1 | Dry
The Chapter “Electricity and Circuits” is the Chapter 12 topic of NCERT Class 6 Science Textbook. Here in Mint Talk India – Prerana Sharma Channel, we have discussed the chapter in multiple… YouTube
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS. 1. Mention two advantages of a dry cell. Ans: 1. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy. 2. It is light and small in size. 2. Learn CBSE
Electricity and Circuits: 6th Class NCERT Science Ch 12
Answer: Circuit diagram showing a bulb connected with a cell. Bulb connected with a cell. Question: What is an electric circuit? Answer: The classed path around which an electric current flows is Class Notes
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Dry Cell Battery
Parts Of An Electric Cell | How It Works
Electric Cell – All You Need To Know!! | Class 6 Electricity And Circuits – Learnfatafat
Electric Cell Diagram Drawing/How To Draw Electric Cell Labeled Diagram Step By Step
How To Draw Diagram Of Dry Cell | How To Draw Dry Cell Diagram
Link to this article: dry cell diagram for class 6.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/