How do you calculate the recoil speed of an atom?
which can be written in terms of the recoil velocity according to,vrecoil=Eγ(me+mp)c. In the last expression, mp is the mass of a proton (i.e. the mass of the nucleus). The expression would get uglier if you used P=mv√1−v2c2 instead of P=mv.
What is the recoil velocity formula?
The recoil velocity of the gun V = − m v M . The negative sign indicates that the gun moves in the opposite direction of motion of the bullet. A bullet is fired from a gun with a velocity 600 m/s. The recoil velocity of the gun is 3 m/s.
When a hydrogen atom is going from n 2 to n 1 its recoil speed?
The recoil speed of hydrogen atom after it emits a photon in going from n=2 state to n=1 state is nearly [Take R∞=1.1×107 m−1 and h=6.63×10−34 Js] 4.5 m s−1.
What is the recoil momentum of a hydrogen atom?
The recoil momentum of H-atom will be. 6.45 x 10−27 N/m.
How is recoil calculated?
We calculate the recoil velocity of the gun and divide it by the time the bullet is accelerating inside the barrel which gives us acceleration in feet-per-second. We then divide that acceleration by g to get the number of g’s the rifle and optic experience.
What is recoil energy of the atom?
In nuclear physics, atomic recoil is the result of the interaction of an atom with an energetic elementary particle, when the momentum of the interacting particle is transferred to the atom as a whole without altering non-translational degrees of freedom of the atom. It is a purely quantum phenomenon.
What is the formula for the recoil energy of the nucleus?
Recoil energy can be calculated using the equation E = (p^2)/2m, where E is the recoil energy, p is the momentum of the nucleus or particle, and m is its mass. This equation is based on the conservation of momentum and energy principles.
What is recoil rate?
Recoil is basically how much the gun bounces everytime you pull the trigger. It differs from gun to gun with the Micro UZI and Vector having the least recoil and guns like the AKM and Gorza having the highest. Recoil recovery rate is how quick the gun can be controlled after recoiling.
What does the recoil velocity depend on?
The recoil velocity results from the force of the throw. Therefore, you need to compare the momentum of the system immediately before the throw to that immediately after. If you look over a longer time interval, you will not be able to ignore the effects of gravity and so cannot use Conservation of Momentum.
When the E of a hydrogen atom jumps from n 4 to n 1?
When an electron jumps from a level n=4 to n=1, the momentum of the recoiled hydrogen atom will be. 13.6×10−27 kg m s−1. Zero. 6.5×10−27 kg m s−1.
When the electron of a hydrogen atom jumps from n 2 to n 1?
If in Hydrogen atom, an electron jumps from n2 = 2 to n1 = 1 in Bohr’s orbit, then the value of wave number of the emitted photon will be (R = 109700 cm–1)
When an hydrogen atom going from n 2 to n 1 emits a photon?
This photon strikes a doubly ionized lithium atom (z=3) in excited state and completely removes the orbiting electron. The least quantum number for the excited state of the ion for the process is. 3.
What is atom recoil velocity?
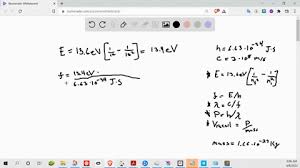
The recoil speed of a hydrogen atom after it emits a photon in going from n=5 state to n=1 state is. 4.178 m s−1.
What is recoil momentum?
Recoil is the backward momentum of a object (like gun)when it is discharged . Recoil velocity of a gun is the velocity by which the gunrecoils after being shot . According to Newton’s third law of motion -every action has an equal and opposite reaction .
What is atom recoil effects?
With effects, we can subscribe to the store and update the atom’s value whenever the store changes. Calling setSelf() from the effect will initialize the atom to that value and will be used for the initial render. If the atom is reset, it will revert to the default value, not the initialized value.
What is the formula for recoil?
Recoil velocity v2= -(m1/m2)v1. Negative sign indicates that recoil velocity is always opposite to the firing velocity.
What is recoil speed?
When a bullet is fired from the gun, due to the reaction force, the gun recoils in the direction opposite to the motion of bullet. The velocity with which it recoils is called as Recoil Velocity.
Is recoil velocity always negative?
Note: Recoil velocity will always be negative as the gun will always move in the opposite direction of the fired bullet.
What is the formula for recoil energy?
In SI (metric) units of measure. Momentum long from: Gun velocity = (bullet mass x bullet velocity) + (powder charge mass x powder charge velocity) / Gun mass x 1000. Then, plug the now known Gun velocity into the translational kinetic energy formula: Recoil energy = 0.5 x Gun mass x Gun velocity2.
What is the maximum recoil speed of the nucleus?
The maximum recoil speed of the nitrogen nuclei was found to be 4.7×106m/s.
What is the momentum of the recoiling nucleus?
Calculating the Magnitude of the Nucleus’ Momentum The magnitude of a vector can be calculated using Pythagoras theorem. Thus, the magnitude p n u c l e u s of the momentum of the recoiling nucleus is ( p x n u c l e u s ) 2 + ( p y n u c l e u s ) 2 .
What is the formula for the recoil energy of an electron?
Show that when a photon of energy is scattered from a free electron at rest, the maximum kinetic energy of the recoiling electron is given by. K max = E 2 E + m c 2 / 2.
What is recoiling electron?
When a gamma-ray photon interacts with a free or loosely bound electron in an atom, it may give up a portion of its energy to this atomic electron. The energy transferred to the electron is a function of the scattered angle of the gamma-ray. This electron may be ejected from the atom and is termed a recoil electron.
Can you calculate recoil?
To calculate recoil energy: Obtain the momentum of the bullet by multiplying the mass and velocity of the projectile fired. Find the product of mass and velocity of the powder charge. Add both the resultants and divide them with the mass of the firearm in grams to get velocity of the firearm.
How is recoil measured?
A standard historical method used to quantify gun recoil is to calculate the “recoil energy” that a shooter absorbs when firing a gun. This calculated recoil energy usually takes into account the primary recoil only, and is a function of the projectile mass, its muzzle velocity and the mass of the firearm.
What is the physics of recoil?
The nature of the recoil process is determined by the force of the expanding gases in the barrel upon the gun (recoil force), which is equal and opposite to the force upon the ejecta. It is also determined by the counter-recoil force applied to the gun (e.g. an operator’s hand or shoulder, or a mount).
What is the formula for recoil energy?
In SI (metric) units of measure. Momentum long from: Gun velocity = (bullet mass x bullet velocity) + (powder charge mass x powder charge velocity) / Gun mass x 1000. Then, plug the now known Gun velocity into the translational kinetic energy formula: Recoil energy = 0.5 x Gun mass x Gun velocity2.
What is the speed of the recoil nucleus?
A nucleus AzX emits an α-particle with velocity v. The recoil speed of the daughter nucleus is: A−44v. 4vA−4.
What is the formula for calculating the recoil of a shotgun?
In other words, you simply square the velocity of recoil, which is easily calculated when we know the weight of the bullet and powder charge and its velocity when exiting from the muzzle. Multiply by the weight of the gun and divide by twice the acceleration of gravity, and you get the recoil energy in foot pounds.
Is there a measurement for recoil?
A standard historical method used to quantify gun recoil is to calculate the “recoil energy” that a shooter absorbs when firing a gun. This calculated recoil energy usually takes into account the primary recoil only, and is a function of the projectile mass, its muzzle velocity and the mass of the firearm.
What is the recoil speed of a hydrogen atom?
What is atomic recoil in physics?
How to find recoil velocity of atom if electron jumps?
Where does energy for recoil speed come from?
Alright, let’s talk about the recoil speed of an atom! It’s a fascinating concept, and it’s all about the fundamental principles of momentum and energy in the world of physics. So, grab your thinking caps, and let’s dive right in!
The Basics: Momentum and Energy
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of the recoil speed formula, let’s get our bearings. We need to understand two key players: momentum and energy.
Momentum is a measure of how much motion an object has. It depends on both the object’s mass and its velocity. The heavier the object or the faster it’s moving, the more momentum it has. We can represent momentum mathematically as p = mv, where p is momentum, m is mass, and v is velocity.
Energy is the ability to do work. We’re going to focus on kinetic energy, which is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. The faster an object is moving, the more kinetic energy it has. The formula for kinetic energy is KE = 1/2 mv², where KE is kinetic energy, m is mass, and v is velocity.
Recoil: It’s All About Conservation!
The concept of recoil is based on a fundamental principle in physics known as conservation of momentum. It states that the total momentum of a system remains constant if no external forces act on it.
Imagine you’re firing a gun. The bullet leaves the barrel with a certain momentum, but to conserve the total momentum of the system (the gun and bullet), the gun recoils in the opposite direction. This recoil is a direct consequence of Newton’s third law of motion, which states that for every action, there’s an equal and opposite reaction.
Deriving the Recoil Speed Formula
Now, let’s get to the heart of the matter—the recoil speed formula. We’ll be using the conservation of momentum principle to derive it.
1. Initial Momentum: Before the atom recoils, the total momentum of the system is zero because everything is stationary.
2. Final Momentum: After the atom recoils, it has a momentum of mv, where m is the mass of the atom and v is its recoil speed.
3. Conservation of Momentum: Applying the conservation of momentum principle, we have:
Initial Momentum = Final Momentum
0 = mv
4. Solving for Recoil Speed: We can rearrange this equation to solve for the recoil speed:
v = 0 / m = 0
This might seem a bit counterintuitive, but it actually makes sense! Since the initial momentum is zero, the final momentum must also be zero. This means that the recoil speed of the atom is also zero.
The Recoil Speed of an Atom Is Always Zero?
Hold on! This answer, v = 0, is true only for a specific scenario—when we consider the atom in isolation, without any other forces acting on it. In reality, there are often other forces involved, like the impact of a photon on the atom.
The Impact of Other Forces
Let’s expand our thinking to include a more realistic scenario, where the atom interacts with something else. Imagine a photon striking the atom. This collision will cause the atom to recoil, and this recoil will have a speed that is not zero.
To account for the impact of other forces, we can modify our formula. Let’s say the incoming particle has a mass of m1 and a velocity of v1. The recoiling atom has a mass of m2 and a recoil velocity of v2. Applying the conservation of momentum principle:
m1v1 + m2v2 = 0
This equation now includes the momentum of the incoming particle. Rearranging to solve for the recoil velocity:
v2 = – (m1v1 / m2)
This equation shows that the recoil speed of the atom is directly proportional to the mass and velocity of the incoming particle and inversely proportional to the mass of the atom.
Important Points to Remember
Here are a few crucial points to keep in mind:
Recoil is a consequence of conservation of momentum.
The recoil speed is always in the opposite direction of the initial motion.
The magnitude of the recoil speed depends on the mass and velocity of the colliding particles.
The recoil speed can be calculated using the conservation of momentum principle.
FAQs
1. What is the recoil speed of a photon?
The recoil speed of a photon is tricky because it’s massless. However, we can talk about its momentum, which is given by p = h/λ, where h is Planck’s constant and λ is the wavelength of the photon.
2. Can the recoil speed of an atom be zero?
Yes, the recoil speed of an atom can be zero if there are no external forces acting on it.
3. What are some examples of recoil in real life?
Here are a few examples:
A gun firing a bullet: The gun recoils backward as the bullet travels forward.
A rocket launching: The rocket expels hot gas downward, causing it to recoil upwards.
A billiard ball hitting another ball: The ball that is hit will recoil backward, while the striking ball will move forward.
4. What are the applications of understanding recoil speed?
Understanding recoil speed has applications in various fields:
Nuclear Physics: Understanding recoil in nuclear reactions is crucial for studying the properties of atoms and nuclei.
Astrophysics: Recoil speed is used to study the movement of stars and galaxies in the universe.
Engineering: The recoil principle is used in designing rockets, guns, and other systems where momentum transfer is important.
5. How does recoil speed affect the accuracy of a firearm?
Recoil speed affects the accuracy of a firearm because it causes the gun to move slightly after firing, which can affect the trajectory of the bullet. This is why many firearms have recoil-absorbing mechanisms to mitigate the effects of recoil.
Let me know if you have any further questions. I’m here to help you explore the exciting world of physics!
See more here: What Is The Recoil Velocity Formula? | Recoil Speed Of Atom Formula
Find recoil speed (approximately in mspace s^{-1}) when
A hydrogen atom emits a photon corresponding to an electron transition from n =5 to n=1. The recoil speed of hydrogen atom is almost (mass of proton = 1.6 × 10 − 27 k g) Toppr
On the recoil and Doppler shifts – University of Strathclyde
The recoil shift due to the flnite mass of an absorbing atom is, when viewed in the right way, simply part of the total Doppler shift. This is true both in the low speed and University of Strathclyde
Where does the kinetic energy of recoil in hydrogen come from?
I came across a rather simple question asking the recoil speed of hydrogen atom when it releases photon while electron goes from n=2 to n=1. The photon emitted Physics Stack Exchange
Mössbauer effect – Deriving the recoil energy formula
I am working on a problem that deals with the Mössbauer effect and calculating the recoil energy on a iron-57 atom, initially at rest and excited to 14.4 keV, Physics Stack Exchange
Recoil Atoms – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Recoil Atoms. The recoil atom produced has a range of about 12nm and causes a dense collision cascade with typically about 2300 displacements (Frenkel ScienceDirect
31.4: Nuclear Decay and Conservation Laws – Physics LibreTexts
E = (Δm)c2. Here, E is the nuclear reaction energy (the reaction can be nuclear decay or any other reaction), and Δm is the difference in mass between initial Physics LibreTexts
Class 12 Physics | Wave Particle Duality | #15 Recoiling of an
PG Concept Video | Wave Particle Duality | Recoiling of an Atom During de-excitation by Ashish Arora Students can watch all concept videos of class 12 Wave YouTube
Recoil Atoms – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The α-decay of the actinides taking place in the crystal lattice creates an alpha particle and a recoil atom. The recoil atom produced has a range of about 12 nm, and causes a ScienceDirect
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
The Recoil Speed Of A Hydrogen Atom After It Emits A Photon In Going From N=5 State To N=1 State Is
Class 12 Physics | Wave Particle Duality | #15 Recoiling Of An Atom During De-Excitation |Jee \U0026 Neet
7 Recoil Speed Of H Atom On Emission Of Photon | Advanced Example | Bohr’S Model | Iit Physic
5. Recoil Speed Of An Atom On Ejection Of Photon
Momentum Cannon Recoil Velocity
Link to this article: recoil speed of atom formula.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/