What is an example of transference and countertransference in nursing?
So let’s say a nurse reminds a patient of their abusive mom and it causes that patient to treat the nurse in a very negative way. That’s an example of transference. And then countertransference is where the nurse’s feelings and response towards the patient are influenced by their past relationships.
What is the key difference between transference and countertransference?
Transference is the redirection of feelings about a specific person onto someone else (in therapy, this refers to a client’s projection of their feelings about someone else onto their therapist). Countertransference is the redirection of a therapist’s feelings toward the client.
What are transference and countertransference and what are their ethical implications?
Transference is identified as unconscious feelings of a client that are felt for another individual of significant importance such as a therapist. Countertransference describes the feelings a therapist may develop for clients they are working with throughout the course of therapy.
What is transference and countertransference in medical?
Transference are the emotions of the patient towards the doctor (positive or negative feelings). 2. Countertransference are the emotional reactions of the doctor towards the patient, such as feelings (frustration) and behaviors (rudeness).
How to remember countertransference vs transference?
Transference is typically seen when a patient is transferring his/her feelings about an individual (e.g., father) onto his/her physician. Countertransference is the unconscious reaction to a patient’s transference or behavior, in which the physician projects his/her feelings, expectations, and desires onto the patient.
How do you avoid transference and countertransference?
Identifying examples of transference and countertransference is a wonderful starting point to prevent negative interference in therapy. Self-reflection, mindfulness, empathy, and ethical boundaries are excellent tools to ensure that when transference arises in session, it is directed in a helpful and therapeutic way.
How to explain countertransference?
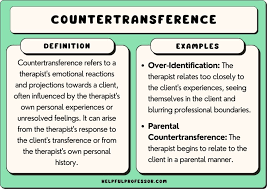
What Is Countertransference? In psychoanalytic theory, countertransference occurs when the therapist projects their own unresolved conflicts onto the client. This could be in response to something the client has unearthed.
Can countertransference be positive?
Positive countertransference might be characterized by intense liking/loving of the patient, desire to be with the patient, and the idealization of the patient’s efforts in psychotherapy. Erotic countertransference is a common manifestation, as is an intense maternal countertransference.
Why is it important to be aware of transference and countertransference?
An awareness of transference and countertransference helps the client see their relationships as repairable, which will ultimately help them approach life with a newfound hope. The therapist can use transference to support their client in developing healthier social and relational interactions across the board.
What is the conclusion of transference and countertransference?
Transference refers to when someone’s emotions and thoughts are unconsciously transferred to another person, and counter-transference occurs when the second person also experiences a similar emotional response. Both these concepts help us comprehend emotional reactions in human interactions.
What is countertransference in nursing?
Countertransference is a psychoanalytical concept which, when applied to nursing, refers to the unconscious response of the nurse to the patient. Psychoanalytical concepts such as the unconscious are infrequently mentioned in the nursing literature and have received little research attention.
What is the difference between transference and countertransference?
Countertransference is essentially the reverse of transference. In contrast to transference (which is about the client’s emotional reaction to the therapist), countertransference can be defined as the therapist’s emotional reaction to the client.
What is transference and countertransference refer to the process by which?
Transference — taking feelings from the past and putting them on someone else (in this case a therapist). Counter-Transference — the therapist (in this case), has their own feelings from the past in reaction to yours. It can get really muddied and confusing. It’s best to try to talk these out with the therapist.
Is countertransference conscious or unconscious?
Sigmund Freud originally developed the concepts of transference and countertransference. He described countertransference as a largely unconscious phenomenon in which the psychologist’s emotions are influenced by a person in therapy, and the psychologist reacts with countertransference.
How can countertransference harm a client?
The Impact of Countertransference Countertransference can significantly damage the therapist-client relationship and can set back treatment. In severe cases, it may introduce new problems that the client must work through with another practitioner. Lesser types of countertransference are quite common, however.
What is countertransference best described as?
White privilege’s impact in the helping relationship. All of thesethe impact personal attitudes have on the provider’s reaction to the client. Countertransference is best described as. the transferring of personal responsibility from the client to the provider.
What is an example of transference in nursing?
Transference occurs all the time in our everyday interactions and is where we may be reminded of someone in the behaviour of others. So specifically in nursing, it is when a patient will view the nurse as someone who is similar to an important person in their life.
How to explain transference to a client?
Transference is often used to describe a redirection of unconscious feelings from their original object to a new object. For example, feelings which originally occurred towards a parent or spouse could then be transferred to a therapist or counsellor within a therapeutic relationship.
What is an example of transference countertransference?
Transference is subconsciously associating a person in the present with a past relationship. For example, you meet a new client who reminds you of a former lover. Countertransference is responding to them with all the thoughts and feelings attached to that past relationship.
How to spot countertransference?
Signs of therapist countertransference Below are several common indicators: Having an excessively critical attitude toward you. Becoming overly invested in your situation. Providing strong judgments on situations and people in your life, independent of your own opinions.
How do you manage countertransference in session?
You can manage transference and countertransference by maintaining professional boundaries, seeking supervision or consultation and reflecting on your reactions to ensure they don’t interfere with your patient’s progress.
How to identify transference?
One tell-tale sign of transference is when your feelings or reactions seem bigger than they should be. You don’t just feel frustrated, you feel enraged. You don’t just feel hurt, you feel deeply wounded in a way that confirms your most painful beliefs.
Which interaction would be considered countertransference?
Countertransference occurs when the nurse unconsciously and inappropriately displaces onto the patient feelings and behaviors related to significant figures in the nurse’s past.
What is transference with example?
Transference in psychoanalytic theory is when you project feelings about someone else onto your therapist. A classic example of transference is when a client falls in love with their therapist. However, one might also transfer feelings of rage, anger, distrust, or dependence.
What is an example of transference in everyday life?
Transference occurs when a person redirects some of their feelings or desires for another person to an entirely different person. One example of transference is when you observe characteristics of your father in a new boss. You attribute fatherly feelings to this new boss. They can be good or bad feelings.
What are transference and countertransference most frequently caused by?
Expert-Verified Answer Transference and countertransference are most frequently caused by Repression and Projection.
What is countertransference in nursing?
How do nurses recognize countertransference?
What is the difference between countertransference and transference to the patient?
What is countertransference therapy?
Hey there! Today, we’re diving into a fascinating topic that’s essential for nurses— transference and countertransference. These concepts are often discussed in psychology, but they play a crucial role in the nurse-patient relationship. Understanding them helps nurses provide better, more compassionate care.
What is Transference?
Imagine you’re a nurse caring for a patient who reminds you of your own grandmother. You might find yourself feeling unusually protective or nurturing towards this patient. This is an example of transference, a phenomenon where patients unconsciously transfer feelings, attitudes, and behaviors from past relationships onto their current nurse.
Think of it like this: We all carry around past experiences that shape how we interact with others. A patient might project their feelings about a strict parent onto a nurse who reminds them of that figure, even if the nurse is completely different.
Examples of Transference
A patient might become angry and demanding towards a nurse who resembles a former boss they disliked.
A patient might become overly dependent on a nurse who reminds them of a caring and supportive family member.
A patient might feel a sense of deep affection for a nurse who reminds them of a past love interest.
It’s crucial to recognize that these feelings are not necessarily about the nurse. They are projections from the patient’s past.
What is Countertransference?
Now, let’s flip the script. Countertransference is the nurse’s unconscious emotional reaction to the patient. It’s essentially the mirror image of transference. When a patient triggers something in a nurse’s past, the nurse might respond in a way that’s not entirely professional.
For instance:
A nurse might become overly protective of a patient who reminds them of a child they lost.
A nurse might feel intense anger towards a patient who reminds them of a difficult ex-partner.
A nurse might develop an inappropriate attachment to a patient who reminds them of someone they admired.
Countertransference can manifest in various ways:
Being overly attentive or neglecting a patient.
Becoming impatient or frustrated.
Feeling overly sympathetic or emotionally drained.
Why is this Important for Nurses?
Understanding transference and countertransference is vital for nurses because it helps them:
Maintain professional boundaries: By recognizing the emotional dynamics at play, nurses can avoid becoming entangled in the patient’s emotional baggage.
Provide objective care: Countertransference can cloud judgment and affect the quality of care. Recognizing and managing these feelings allows nurses to provide unbiased care.
Build therapeutic relationships: Acknowledging and addressing these unconscious reactions fosters trust and a healthy nurse-patient relationship.
Managing Transference and Countertransference
So, how do nurses navigate these complex emotional dynamics? Here’s a breakdown:
1. Self-Awareness:
Reflect on your own past experiences and relationships. How might these influence your interactions with patients?
Pay attention to your emotional responses to patients. Are you experiencing feelings that seem out of place?
2. Supervision:
Seek guidance from a therapist or supervisor. They can help you process your emotional reactions and develop strategies for managing countertransference.
Discuss your experiences with colleagues. Sharing your observations and concerns can provide valuable insights and support.
3. Professional Boundaries:
Maintain a professional distance. Avoid personalizing your interactions with patients and focus on their needs.
Set limits and enforce them. It’s okay to say no to requests that are inappropriate or compromise your professional role.
4. Mindfulness and Self-Care:
Practice mindfulness and self-care. This involves taking time to recharge and attend to your own emotional well-being.
Recognize when you need a break. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, step back and take a moment to regroup.
5. Collaboration:
Communicate with the patient’s family and other healthcare professionals. Working together can provide a broader perspective and support.
Refer patients to appropriate specialists. If a patient’s emotional needs are complex, seek professional help.
The Importance of Awareness
Transference and countertransference are natural human responses. They aren’t necessarily a bad thing, but they can have a significant impact on the nurse-patient relationship. By developing self-awareness, practicing good boundaries, and seeking support, nurses can navigate these dynamics effectively and provide the best possible care to their patients.
FAQs:
Q: Can transference and countertransference be beneficial?
A: In some cases, transference can actually be helpful. A patient might feel more comfortable opening up to a nurse who reminds them of a trusted friend. However, it’s essential to maintain a professional distance and not get caught up in the patient’s projections.
Q: Can I tell my patients about transference and countertransference?
A: It’s generally not advisable to directly explain these concepts to patients. While you can acknowledge that everyone brings their past experiences into their relationships, keep the focus on the patient’s needs and the therapeutic relationship.
Q: What are some signs of countertransference?
A: Common signs of countertransference include feeling overly attached to a patient, becoming overly critical, experiencing intense emotions (like anger or sadness), or neglecting a patient’s needs.
Q: How can I avoid countertransference?
A: You can’t entirely avoid countertransference, but you can manage it by practicing self-awareness, seeking supervision, maintaining boundaries, and prioritizing self-care.
Q: Can countertransference be resolved?
A: Countertransference can be managed and resolved through self-awareness, professional supervision, and open communication.
Remember, the goal is to recognize these dynamics, manage them effectively, and provide the best possible care to our patients.
See more here: What Is The Key Difference Between Transference And Countertransference? | Transference And Countertransference In Nursing
Transference vs. Countertransference in Nursing – LevelUpRN
Countertransference refers to when patient reminds the nurse of someone in their life. What is Countertransference in Nursing? Countertransference in nursing is whenever the nurse unknowingly transfers their unresolved thoughts, feelings, and Level Up RN
Managing Transference and Countertransference in Cognitive
Countertransference occurs when the therapist responds complementary to the patient’s transference based on their own dysfunctional beliefs or assumptions. National Center for Biotechnology Information
Therapeutic relationships | Nurse Key
Countertransference. Countertransference occurs when the nurse unconsciously and inappropriately displaces onto the patient feelings and behaviors Nurse Key
(PDF) Transference, counter-transference and repetition: Some …
Recognizing possibilities of transference, counter-transference along with repetitive patterns of behaviours, can help nurses of all specialities to address situations ResearchGate
Transference and countertransference – PubMed
Topic: The utility of transference and countertransference in professional nursing relationships. Purpose: To provide an introductory text for nurses new to these concepts. PubMed
Full article: Managing Transference and Countertransference in …
Countertransference occurs when the therapist responds complementary to the patient’s transference based on their own dysfunctional beliefs or assumptions. Transference Taylor & Francis Online
Countertransference in the nurse‐patient relationship: a review of
The nurse’s countertransference has many expressions. The literature under review has highlighted the expression of countertransference through physical Wiley Online Library
Countertransference in the nurse-patient relationship: a … – PubMed
Countertransference is a psychoanalytical concept which, when applied to nursing, refers to the unconscious response of the nurse to the patient. Psychoanalytical concepts PubMed
Transference and Countertransference – Jones – 2004
TOPIC The utility of transference and countertransference in professional nursing relationships. PURPOSE To provide an introductory text for nurses new to Wiley Online Library
Transference, counter-transference and repetition: some
Background. The literature suggests that transference can be a source of creativity as well as destructiveness and influence important communications with oneself and others ResearchGate
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Nurse/Client Relationship, Therapeutic Communication -Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing |@Leveluprn
Therapeutic Communication Techniques Nursing | Mental Health Nclex Tips
What Is The Difference Between Transference And Countertransference?
Therapist Explains Transference \U0026 Countertransference
Transference And Countertransference/ Psychiatric Problems
Link to this article: transference and countertransference in nursing.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/