What attaches to the suprasternal notch?
Inferior to the hyoid bone, the superficial or investing layer of the deep cervical fascia divides into anterior and posterior leafs to attach to the respective borders of the suprasternal (jugular) notch, forming a small space ~2 cm superior to the manubrium 1–3.
What does a suprasternal notch articulate to?
The suprasternal notch (jugular notch) is at the superior segment of the manubrium sterni. On either side, the left and right clavicular notches are present. The clavicular notches of the sternum articulate with the medial end of each clavicle to form the sternoclavicular joints.
What is 5cm below the suprasternal notch?
&sternalangle=The sternal angle is the bony horizontal ridge that joins the manubrium to the body of the sternum and is approximately 5 cm below the suprasternal notch. It articulates with the second rib and therefore is a useful landmark for numbering ribs and interspaces.
What is a lump in the sternal notch?
A mass at the sternal notch suggests a tuberculous abscess, dermoid cyst, or a fatty tumor associated with Cushing’s syndrome similar to the Dowager’s hump. Fullness of the sternal notch can occur in leukemia (Jaccoud’s sign). Lateral neck masses.
Why is the suprasternal notch important?
The jugular notch is a shallow, visible dip located at the top center of the thorax, between the ends of the clavicle bones, directly above the sternum. It serves as an important anatomical landmark for identifying structures within the neck and thoracic region.
What causes pulsation in the suprasternal notch?
It is also important to palpate the suprasternal notch and the 1st and 2nd right intercostal spaces. A significant pulsation here can indicate an ascending aortic aneurysm as the cause for the aortic regurgitation. Ascending aortic aneurysm: pulsations in the right upper ICS and sternal notch.
What’s behind your sternum?
Your thymus gland is located behind your sternum (breastbone). This gland is part of your lymphatic system.
What artery is in the suprasternal notch?
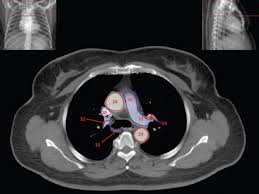
The arterial structures consist of the aortic arch, brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian arteries and their branches. The aortic arch initially ascends posterior to the superior vena cava, then turns inferiorly as it passes anterior and to the left of the vertebral column.
What does the suprasternal space contain?
According to Gray’s Anatomy, it contains a small amount of areolar tissue, the lower parts of the anterior jugular veins, and the jugular venous arch, as well as the sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscles and occasionally lymph nodes (14).
What is the landmark for the suprasternal notch?
The suprasternal notch is a visible dip in between the neck, between the clavicles, and above the manubrium of the sternum. It is at the level of the T2 and T3 vertebrae. The trachea lies just behind it, rising about 5 cm above it in adults.
Why is suprasternal space called space of burns?
The suprasternal space (Space of burns) is a narrow space between the superficial and deep layers of the investing layers of the deep cervical fascia. Boundaries: Anterior: superficial layer of deep cervical fascia attached to the anterior border of the manubrium.
What is another name for the suprasternal notch?
The suprasternal notch, also known as the fossa jugularis sternalis, or jugular notch, is a large, visible dip in between the neck and the two collarbones of the human anatomy.
Is it normal to feel a lump under sternum?
The small hard lump at the lower end of the sternum (breastbone) is normal. It is called the xiphoid process. You can feel it. It is more prominent in babies and slender children.
What is a fatty lump below the sternum?
In an epigastric hernia, fat pushes out through a weakness in the wall of your abdomen between your belly button and sternum and forms a lump.
What causes suprasternal swelling?
Causes of suprasternal swelling apparent only during valsalva maneuver in a child include apical lung herniation, jugular venous aneurysms and laryngocele, apart from cervical thymic herniation [2, 3].
What are the symptoms of suprasternal notch?
All forms of dysphagia are often referred to the suprasternal notch or neck. Concurrent neurologic symptoms, nasopharyngeal regurgitation, dysphonia, drooling, aspiration, and coughing after eating suggest OPD.
How do you palpate the suprasternal notch?
The suprasternal notch is examined from behind. It is felt as a smooth concavity lying between the origins of the two sternocleidomastoid muscles, medial to the sternoclavicular joints. Disruption of the smooth contour may indicate sternoclavicular dislocation.
Why do we palpate the sternal notch?
To verify a safe location of the endotracheal tube (ETT), palpation of the ETT at the sternal notch is a time-honored technique: After anesthetic induction and confirmation of orotracheal intubation, the patient’s head is placed in a neutral position.
What is the hole between your collarbones called?
noun. : the depression in the top of the sternum between its articulations with the two clavicles. called also jugular notch.
Is it normal to see my pulse in my neck?
You may feel your pulse in the arteries of your neck or throat. Sometimes you can even see the pulse as it moves the skin in a more forceful way.
What is dysphagia at sternal notch?
Signs and symptoms Patients usually complain of dysphagia (the feeling of food getting stuck several seconds after swallowing), and will point to the suprasternal notch or behind the sternum as the site of obstruction.
Why does it feel like something is stuck behind my sternum?
Dysphagia from GERD This form of acid reflux causes the contents of your stomach to flow back up into your esophagus, which irritates the lining. “This can cause a burning sensation in the throat and neck, coughing or a nagging feeling that something is stuck behind your breastbone,” Dr. Lee explains.
Why does it hurt behind my sternum?
What causes pain in the sternum? Many conditions can cause pain in the sternum, including injuries, pneumonia, bronchitis, and costochondritis. Gastrointestinal problems, such as acid reflux, can cause pain behind the sternum. People may believe that their sternum pain is a heart attack symptom.
What organ is directly behind the sternum?
The thymus gland is in the chest between the lungs. It makes white blood cells (T lymphocytes) which are part of the immune system and help fight infection. The thymus gland is in the chest, between the lungs and behind the breastbone or sternum.
Can suprasternal pulsation be normal?
In a young normal person there should be no palpable pulse. A prominent pulse may be indicative of an uncoiled aorta,arch aneurysm, or a tortuous blood vessel. The most likely cause of a suprasternal pulse in an adult is an aortic arch aneurysm, while the most likely cause in a child is coarctation of the aorta.
What does suprasternal notch articulate to?
Jugular notch (aka, suprasternal notch) is on the superior border of the manubrium. Clavicular notches are to the sides of the jugular notch; these are where the clavicles (aka, collarbones), articulate with the sternum. Costal notches articulate with the costal cartilages of the ribs (“costal” refers to the ribs).
What is the suprasternal space of burns?
Anatomically, the suprasternal space (SSS) of Burns contains a small amount of areolar tissue, the lower parts of the anterior jugular veins (AJVs), and the jugular venous arch, as well as the sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscles, interclavicular ligament, and sometimes a lymph node (LN) (Fig.
What attaches to the sternal angle?
The sternal angle marks the point at which the costal cartilage of either second rib articulates with the sternum. During physical examinations, the readily palpated sternal angle is thus used as a landmark to identify the 2nd rib, and by extension, by counting, also the remaining ribs.
What attaches to the clavicular notch?
The medial end is also known as the sternal end. It is quadrangular and articulates with the clavicular notch of the manubrium of the sternum to form the sternoclavicular joint.
What does the jugular notch connect to?
The jugular notch provides an attachment site for the interclavicular ligament.
What structure is related to the suprasternal notch?
Structure. The suprasternal notch is a visible dip in between the neck, between the clavicles, and above the manubrium of the sternum. It is at the level of the T2 and T3 vertebrae. The trachea lies just behind it, rising about 5 cm above it in adults.
What is a suprasternal notch?
What is the jugular notch of the sternum?
What is suprasternal notch & jugular notch?
How do you find a suprasternal notch?
Think of it like a doorway. Behind that notch, you’ll find the superior mediastinum, which is basically the space between your lungs. It’s where all sorts of essential structures hang out. Let’s explore what’s hiding behind this anatomical gateway:
The Key Players Behind the Suprasternal Notch
The Thymus: This little gland, sitting right behind the notch, plays a big role in your immune system, especially when you’re a kid. It’s responsible for making those special cells called T-lymphocytes that help fight off infections. Think of it as your body’s own personal army.
The Great Vessels: These are the big blood vessels that carry blood to and from your heart. Right behind the notch, you’ll find the brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery. These arteries are responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to your head, neck, and arms. And don’t forget the superior vena cava, which carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
The Vagus Nerve: This important nerve is responsible for controlling a wide range of bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It also carries sensory information from your internal organs.
The Trachea: This is your windpipe, the passageway that carries air to your lungs. You can feel the trachea right below the suprasternal notch if you swallow.
The Esophagus: This muscular tube carries food from your mouth to your stomach. You can’t actually feel the esophagus, but it’s nestled behind the trachea.
A Visual of the Suprasternal Notch and its Surroundings
Imagine the suprasternal notch as the entrance to a busy street. The thymus is like a small building on the corner, while the great vessels are like a network of large pipes carrying water throughout the neighborhood. The vagus nerve is like a series of cables connecting different parts of the city, and the trachea and esophagus are like two tunnels transporting air and food.
Why is the Suprasternal Notch Important?
Besides being a cool anatomical landmark, the suprasternal notch is important for several reasons:
Medical Procedures: Doctors use the suprasternal notch to locate other anatomical structures during medical procedures, especially those involving the chest. Think of it like a map for medical professionals.
Chest Compression: During CPR, the suprasternal notch is the point where you apply pressure to the chest to help circulate blood. This is crucial in emergency situations to keep the heart beating.
Positioning: It’s a useful reference point when positioning patients for medical exams or surgery. This helps ensure the patient is positioned correctly and comfortably.
FAQs about the Suprasternal Notch
1. Can I Feel My Thymus Behind the Suprasternal Notch?
Unfortunately, no. The thymus is a small, soft gland that’s tucked away behind the breastbone. You can’t feel it.
2. What Happens If There’s Something Wrong with the Structures Behind the Suprasternal Notch?
Depending on the specific structure involved, problems behind the suprasternal notch can cause a range of symptoms, like difficulty breathing, chest pain, swelling in the neck, or a change in your voice. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
3. What Can I Do to Take Care of the Structures Behind the Suprasternal Notch?
There’s no special care you need to take to protect the structures behind the suprasternal notch. Living a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, helps keep your entire body healthy, including the area behind the suprasternal notch.
4. Can I See My Suprasternal Notch in the Mirror?
Yes, if you look in the mirror and tilt your head back slightly, you can usually see the notch at the top of your breastbone.
5. How Can I Find My Suprasternal Notch?
The suprasternal notch is easy to find. Feel for the bony prominence in the middle of your neck, just below your Adam’s apple. Now, gently slide your fingers down the bony structure (your sternum) until you feel a small dip. That’s your suprasternal notch.
Understanding the suprasternal notch is like having a little cheat sheet to the anatomy of your chest. It’s a gateway to a whole world of important structures that keep you alive and functioning. So, next time you feel your necklace resting on that little dip at the top of your breastbone, remember that it’s not just a bony landmark, but a gateway to the heart of your being.
See more here: What Does A Suprasternal Notch Articulate To? | What Is Behind The Suprasternal Notch
Suprasternal Notch – Location, Function and Pictures
What is Suprasternal Notch? It is defined as a large, prominent dip on the apex of the sternum in the middle of articulation along with two clavicles. It is a significant division of the human anatomy. In KnowYourBody.net
Suprasternal Notch – Location, Anatomy, Clinical Significance,
The suprasternal notch, also known as the jugular notch or jugular notch of the manubrium, is an anatomical feature located at the superior part of the sternum, Medical Treasure
Jugular Notch of Sternum | Complete Anatomy – Elsevier
The jugular notch of the sternum (suprasternal or presternal notch) is the large indentation found along the superior border of manubrium of the sternum. It is located Elsevier
Suprasternal notch (examination) – GPnotebook
The suprasternal notch is examined from behind. It is felt as a smooth concavity lying between the origins of the two sternocleidomastoid muscles, medial to GPnotebook
Anatomy, Thorax, Sternum – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
The suprasternal notch (jugular notch) is at the superior segment of the manubrium sterni. On either side, the left and right clavicular notches are present. The clavicular notches of the sternum National Center for Biotechnology Information
Sternum: Anatomy, parts, pain and diagram | Kenhub
Bone marrow biopsy. Pectus excavatum. Pectus carinatum. Sources. + Show all. Embryology. The sternum develops from a left and right cartilaginous plates Kenhub
Anatomy, Thorax, Xiphoid Process – StatPearls
The manubrium is the broad, quadrangular, and most superior segment and is characterized by its superior dip known as the suprasternal notch. The body is the middle and longest part and National Center for Biotechnology Information
Jugular notch of sternum – e-Anatomy – IMAIOS
The jugular notch (suprasternal notch, presternal notch) is at the center of the superior border of the manubrium of sternum. IMAIOS
See more new information: pilgrimjournalist.com
Suprasternal Notch Palpation
Jugular Notch Palpation
Surface Marking Of Jugular Notch ||Anatomy Of Jugular Notch ||
Suprasternal Notch | Anatomical Terms Pronunciation By Kenhub
What Is The Suprasternal Notch?
Link to this article: what is behind the suprasternal notch.
See more articles in the same category here: https://pilgrimjournalist.com/wiki/