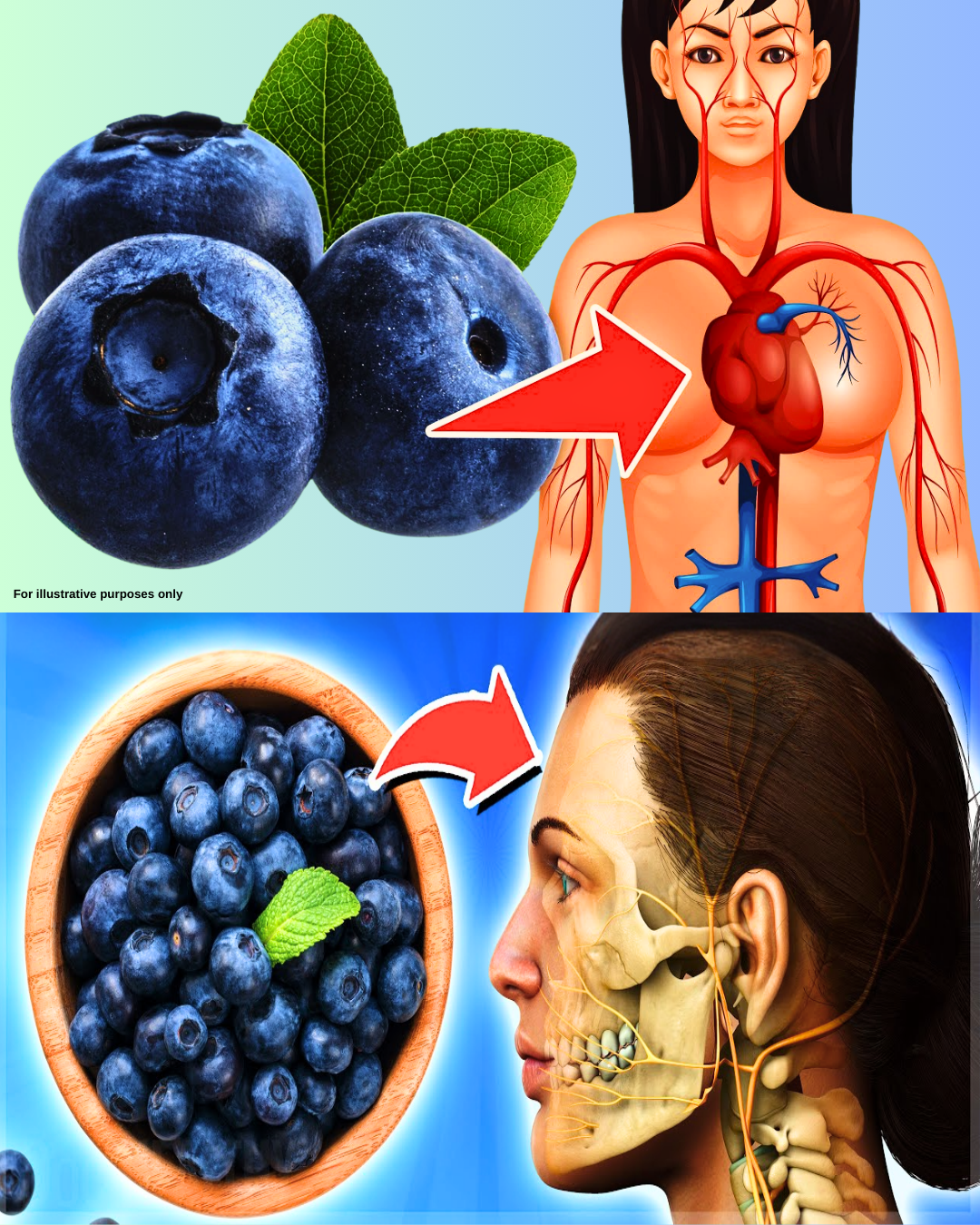
Blueberries-those small, vibrant fruits that peak in the warmer months-have quietly become nutrition superstars. Whether you snack on them, blend them into smoothies, or sprinkle them on salads, they offer far more than just sweetness.
Let’s explore what daily blueberry consumption can do for your health, and why nutrition experts continue to recommend them.

A Nutritional Powerhouse in Every Bite
For illustrative purposes only.
Blueberries are packed with vitamins, minerals, ber, and powerful plant compounds. Their deep blue
color comes from anthocyanins—polyphenols known for their health-promoting effects. These
compounds support everything from heart health to brain function.
Why Blueberries Deserve a Daily Spot on Your Plate
1. Cardiovascular Support
Blueberries are known to support cardiovascular health. Research shows that regular intake may reduce
the risk of heart disease. Anthocyanins help maintain exible blood vessels, promote healthy circulation,
and may assist in managing cholesterol. Some studies suggest heart health markers can improve in just
six weeks of consistent consumption.
2. Brain and Cognitive Function
Often dubbed “brain food,” blueberries may help slow cognitive decline and boost memory, especially
with age. Their avonoids protect neurons and may improve communication between brain cells—
making them a smart choice, particularly for those with a family history of memory issues.
3. Blood Sugar Balance
Despite their natural sweetness, blueberries may help regulate blood sugar.
Studies highlight their role in enhancing insulin sensitivity and improving
glucose metabolism, making them a great option for those monitoring blood
sugar levels.
4. Digestive Health and Gut Microbiome
Blueberries also support gut health. Their ber and polyphenols nourish
benecial gut bacteria and may encourage a healthier, more diverse
microbiome—key for digestion and overall wellness.
5. Exercise Recovery
Blueberries might aid post-workout recovery. Emerging research suggests
their antioxidants help reduce inammation and muscle soreness, making
them especially helpful for athletes or active individuals.
The Best Ways to Enjoy Blueberries
Fresh blueberries offer the most nutritional benet—eat them as-is, add to
salads, or top oatmeal and yogurt. Frozen blueberries are also a convenient
and healthy alternative, retaining most of their nutrients.
For optimal health benets, avoid sugary desserts or fried foods featuring
blueberries, as those forms don’t deliver the same value as eating them whole.

What Happens If You Eat Blueberries Every Day?
Making blueberries a daily habit can lead to a cascade of positive effects.
Here’s what the science says:
- Antioxidant Boost: Blueberries are rich in antioxidants, which help
neutralize harmful molecules in the body. This can translate to less
inammation and a lower risk of chronic conditions. - Heart Health: Regular consumption supports healthy blood pressure and
cholesterol, while also helping blood vessels stay exible and resilient. - Brain Support: Daily blueberry intake may help preserve cognitive
function, especially in older adults. - Blood Sugar Regulation: Blueberries can help keep blood sugar levels
steady, thanks to their unique blend of ber and polyphenols. - Digestive Wellness: The ber in blueberries supports regularity and a
healthy gut environment. - Low Calorie, High Satisfaction: A cup of blueberries delivers about 80
calories, 4 grams of ber, and a quarter of your daily vitamin C needsmaking them a satisfying and nutrient-dense snack.
For illustrative purposes only.
It’s important to note that while blueberries offer a host of benets, they work
best as part of a varied, balanced diet. Relying on any single food, no matter
how healthy, can lead to nutritional gaps.
How Much Should You Eat?
Research suggests ½ to 2 cups per day is benecial. A ½-cup serving is a
practical, effective goal for most people, depending on age, activity, and overall
dietary needs.
Can You Have Too Many Blueberries?
As tempting as it may be to devour an entire pint in one go, moderation is key.
Overindulgence can lead to a few minor issues:
- Digestive Discomfort: The ber in blueberries is great for your gut, but too
much at once can cause bloating or other gastrointestinal complaints. - Sugar Load: While blueberries have less sugar than many other fruits,
eating them in excess can still contribute to a higher overall sugar intake. - Kidney Stones: Blueberries contain oxalates, which in very large amounts
could raise the risk of kidney stones for susceptible individuals. - Stick to recommended portions and pair blueberries with a variety of other
nutrient-rich foods for the best results.